UK unveils cybersecurity initiative with £210 million funding to enhance public sector defenses
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: UK announces plan to strengthen public sector cyber defenses
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The United Kingdom has launched a £210 million initiative to enhance cybersecurity across its public sector, establishing a Government Cyber Unit and implementing new security standards. This move aims to protect critical services from cyber threats, with moderate confidence that it will improve resilience against cyberattacks. Key stakeholders include government departments, public service users, and private sector partners.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The UK’s new cybersecurity strategy will significantly enhance public sector resilience against cyber threats. Supporting evidence includes the substantial financial investment and the establishment of a dedicated cyber unit. However, uncertainties remain regarding the effective implementation and coordination across diverse government departments.
- Hypothesis B: The strategy will have limited impact due to potential bureaucratic inefficiencies and the evolving nature of cyber threats. This is supported by historical challenges in public sector cybersecurity initiatives and the rapid advancement of cyberattack techniques.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the comprehensive nature of the plan and the involvement of major cybersecurity firms. Indicators such as successful implementation of security standards and improved incident response capabilities could further support this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The allocated budget will be effectively utilized; government departments will cooperate with the new cyber unit; private sector partners will actively contribute to the initiative.
- Information Gaps: Details on the specific measures and timelines for implementation; metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of the strategy.
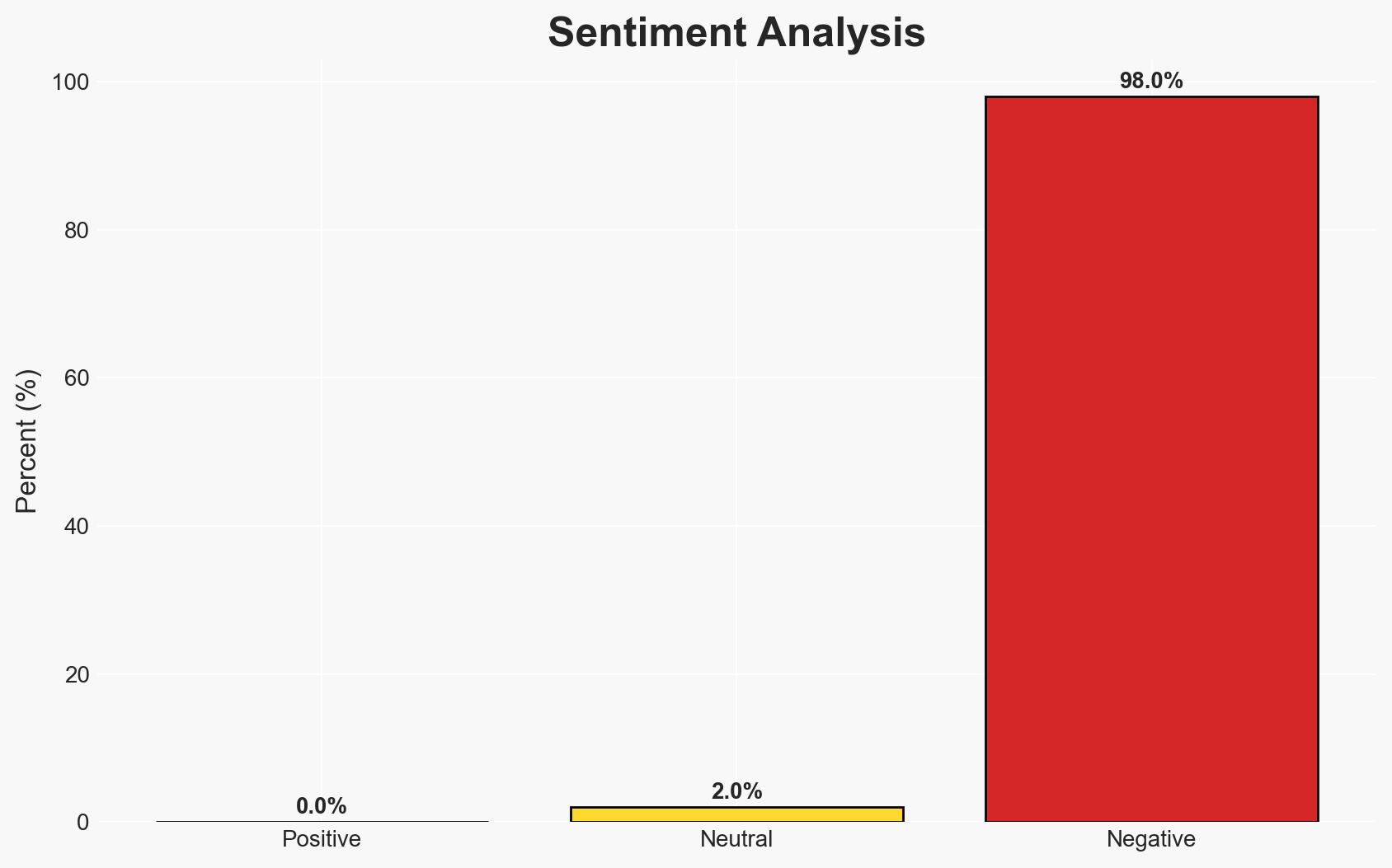
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on public statements without independent verification; risk of underestimating adversary capabilities and adaptability.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased cybersecurity resilience in the UK public sector, potentially setting a precedent for other nations. However, failure to adapt to evolving threats could undermine these efforts.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened cyber defenses may deter state-sponsored cyberattacks, influencing geopolitical dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced cybersecurity could reduce vulnerabilities exploited by terrorist organizations for disruptive activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: The initiative may prompt adversaries to develop more sophisticated cyberattack methods.
- Economic / Social: Improved cybersecurity could enhance public trust in digital services, but failure could lead to economic disruptions and social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor implementation progress, engage with private sector partners, and establish clear metrics for success.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, foster international cybersecurity partnerships, and enhance public awareness campaigns.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful implementation leads to reduced cyber incidents. Worst: Bureaucratic delays and evolving threats undermine efforts. Most-Likely: Gradual improvement with ongoing challenges in threat adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Ian Murray, Digital Government Minister
- Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, Sage, NCC Group, Santander (as Software Security Ambassadors)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
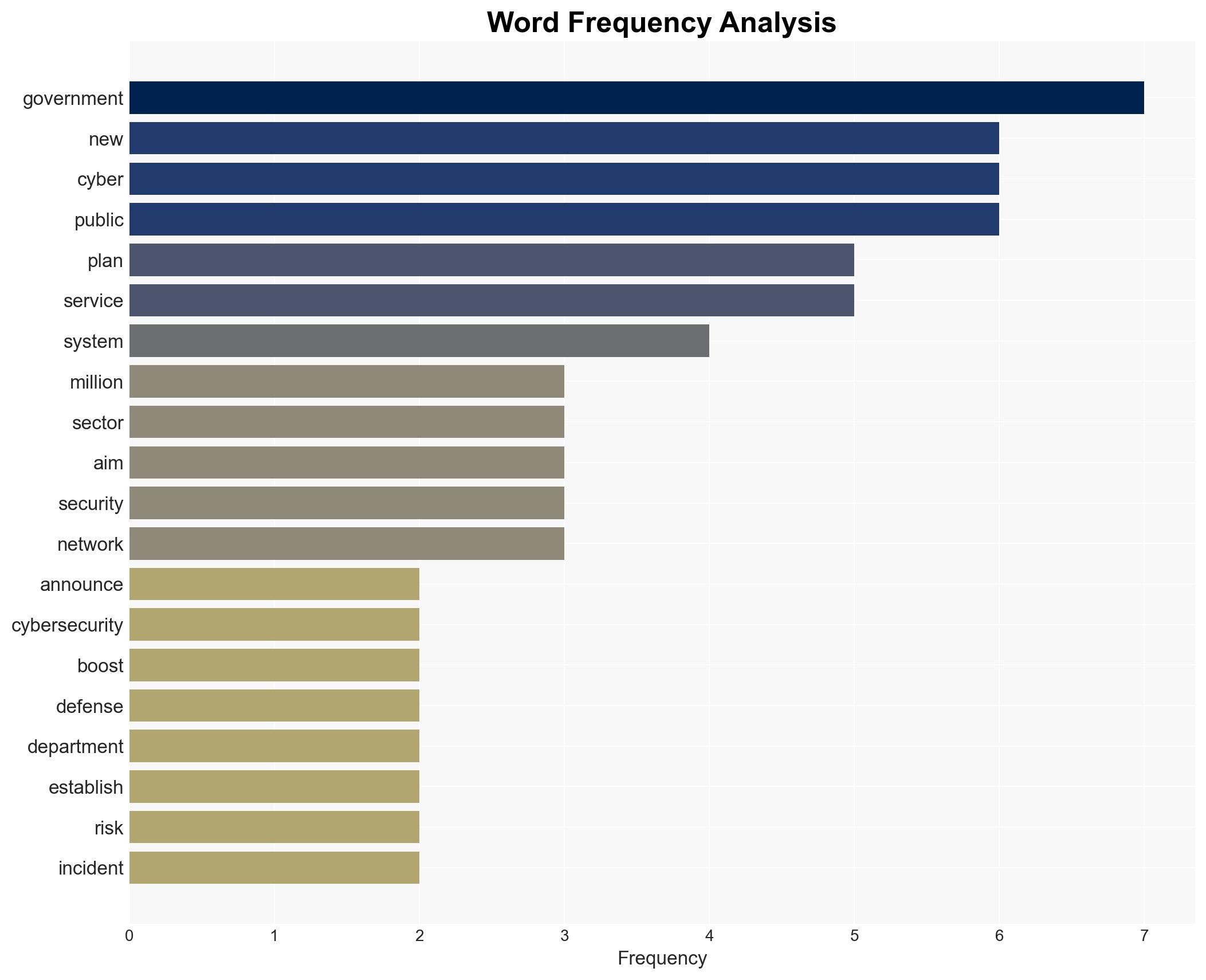
cybersecurity, public sector, cyber defense, UK government, cyber resilience, public-private partnership, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us