UN cybercrime pact to be signed in Hanoi raises hopes concerns – The Times of India
Published on: 2025-10-22
Intelligence Report: UN Cybercrime Pact to be Signed in Hanoi Raises Hopes and Concerns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The upcoming signing of the UN cybercrime pact in Hanoi presents both opportunities and risks. The most supported hypothesis suggests that the pact aims to enhance global cyber defense cooperation, albeit with significant concerns regarding human rights implications. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Engage in diplomatic dialogue to ensure human rights safeguards are prioritized and monitor the implementation closely.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The UN cybercrime pact is primarily a tool for enhancing international cooperation against cybercrime, aiming to reduce its economic impact and improve global cybersecurity resilience.
Hypothesis 2: The pact is a veiled attempt to increase state surveillance capabilities under the guise of cybersecurity, potentially infringing on human rights and freedom of expression.
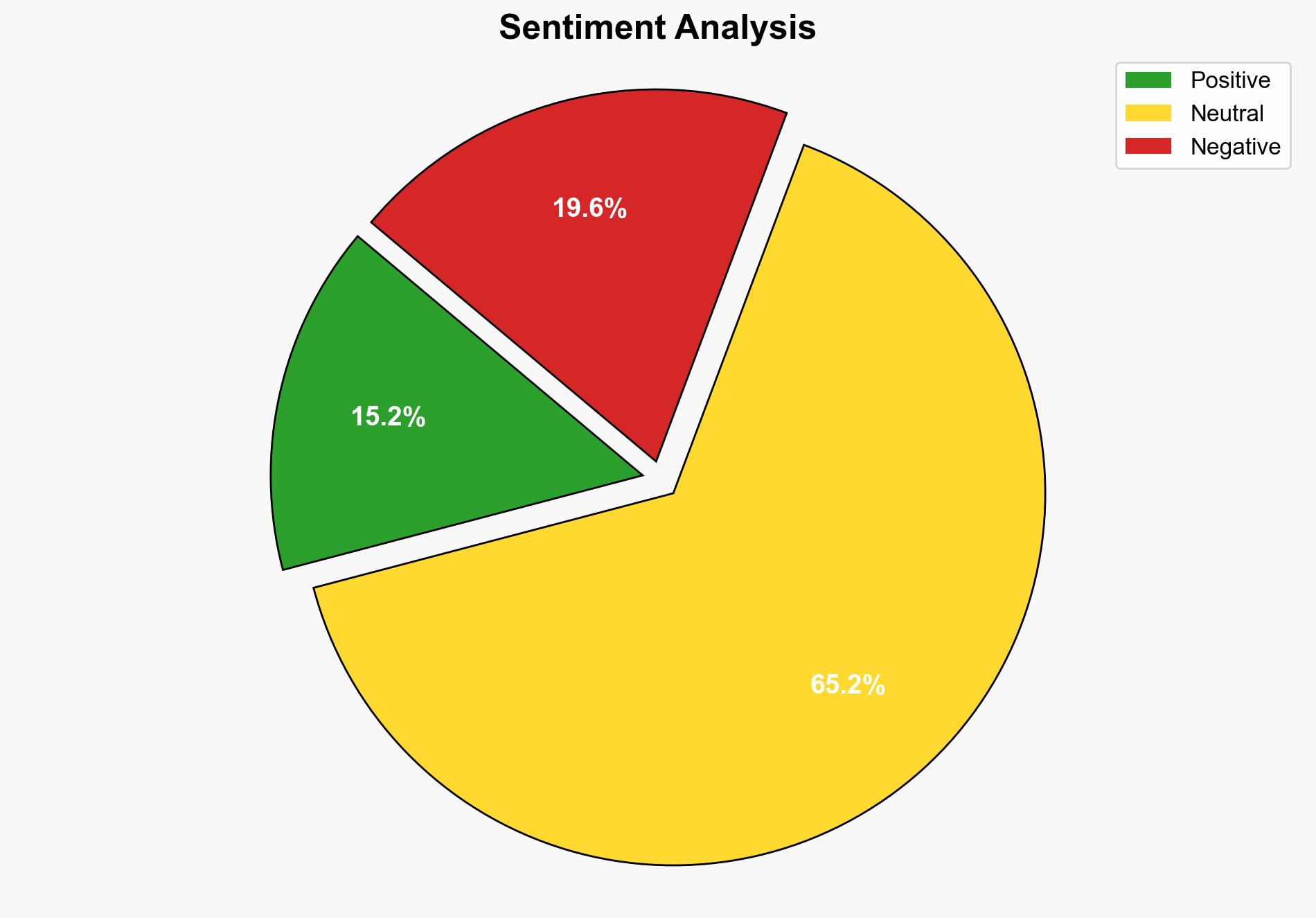
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported by the inclusion of provisions to protect human rights and the involvement of major international entities like the European Union and Canada. However, Hypothesis 2 is supported by criticisms from human rights organizations and tech companies, highlighting the potential for abuse of vague legal definitions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions for Hypothesis 1 include the belief that international cooperation will be effective and that human rights safeguards will be enforced. For Hypothesis 2, assumptions include the potential for states to exploit the treaty for surveillance. Red flags include Vietnam’s human rights record and the lack of transparency in treaty negotiations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The treaty could lead to improved global cyber defenses, reducing economic losses from cybercrime. However, it risks legitimizing state surveillance and curtailing civil liberties, potentially leading to international criticism and diplomatic tensions. The broad definitions of cybercrime could also criminalize legitimate cybersecurity research.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage with international partners to advocate for clear definitions and robust human rights protections within the treaty.
- Monitor implementation to ensure compliance with international human rights standards.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: The treaty strengthens global cyber defenses without infringing on human rights.
- Worst Case: The treaty becomes a tool for state surveillance, leading to widespread human rights abuses.
- Most Likely: Mixed outcomes with improved cybersecurity but ongoing human rights concerns.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Antonio Guterres, Raman Jit Singh Chima, Le Xuan Minh, Meta, Microsoft, Human Rights Watch.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus