UN peacekeeping forces to be cut 25 due to budget strains Official – The Times of India
Published on: 2025-10-09
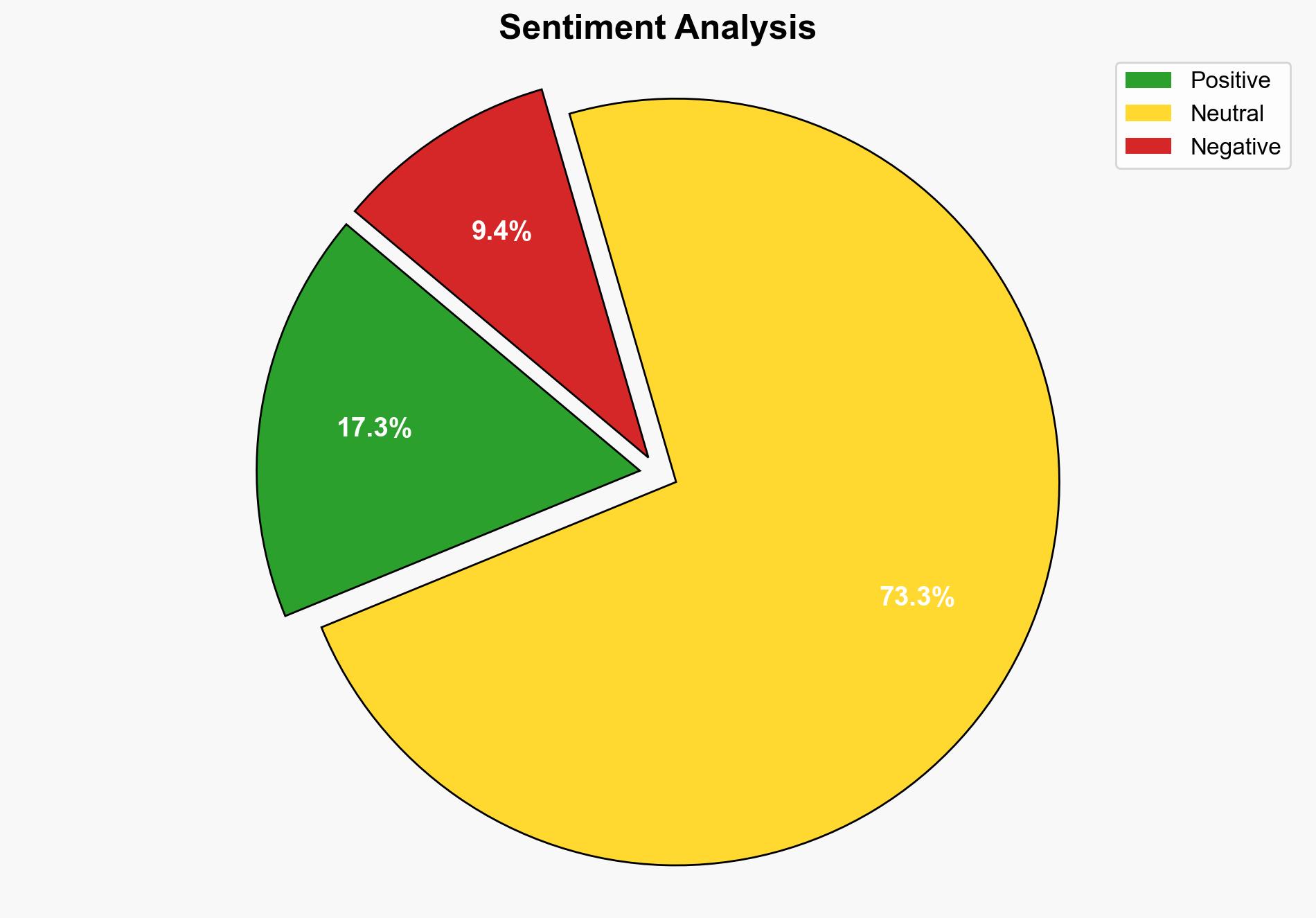
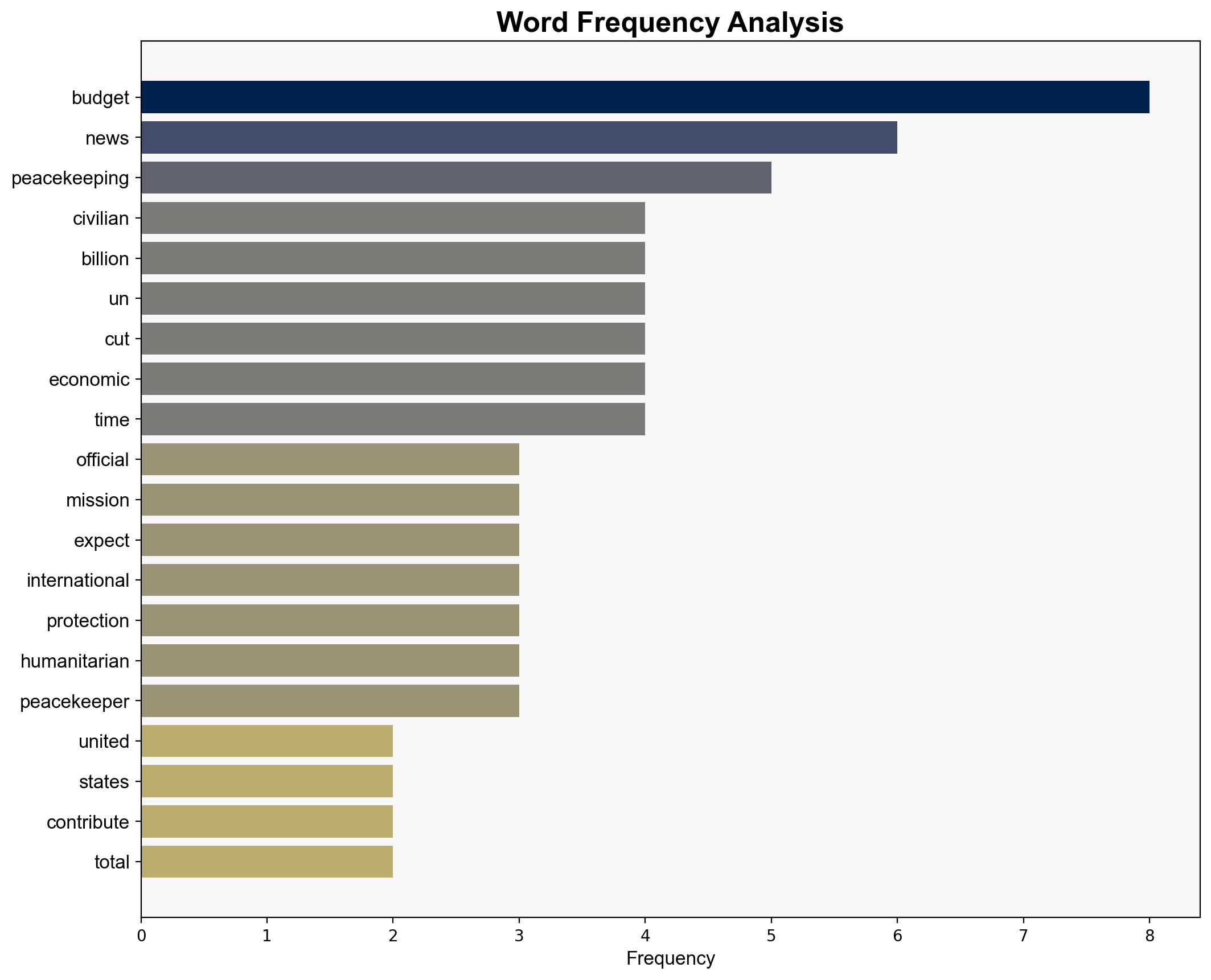
Intelligence Report: UN Peacekeeping Forces to be Cut 25% Due to Budget Strains – The Times of India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that the budget cuts to UN peacekeeping forces are primarily driven by financial constraints and political pressure from major contributors like the United States. This report uses structured analytic techniques to evaluate the situation, concluding with a moderate confidence level. It is recommended that stakeholders prioritize essential humanitarian and protection activities while seeking alternative funding sources to mitigate the impact of these cuts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The budget cuts are primarily a result of financial constraints and political pressure from major contributing countries, particularly the United States, which has historically criticized international institutions for inefficiency.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The budget cuts are strategically motivated to reallocate resources towards emerging security threats, such as the new international anti-gang mission in Haiti, reflecting a shift in priority rather than purely financial considerations.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the evidence of the U.S. administration’s stance on international contributions and the explicit mention of budgetary shortfalls. Hypothesis B lacks substantial evidence in the provided text to suggest a strategic reallocation focus.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**:
– Hypothesis A assumes that financial constraints are the primary driver without considering potential strategic shifts.
– Hypothesis B assumes a strategic reallocation without clear evidence of new threat prioritization.
– **Red Flags**:
– Lack of detailed breakdown of how cuts will affect specific missions.
– Absence of official statements from other major contributors like China.
– Potential bias in reporting due to political narratives surrounding international contributions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Reduced peacekeeping presence may lead to increased instability in regions like South Sudan and the Democratic Republic of Congo, potentially escalating conflicts.
– **Humanitarian Risks**: Diminished protection for civilians and humanitarian convoys could exacerbate humanitarian crises.
– **Economic Risks**: Shortfalls in funding could strain local economies reliant on peacekeeping missions.
– **Psychological Risks**: Perception of reduced international commitment may embolden hostile actors in conflict zones.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage with international partners to explore alternative funding mechanisms to sustain critical peacekeeping operations.
- Develop contingency plans for regions most affected by troop reductions, prioritizing civilian protection and humanitarian aid.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Successful reallocation of resources with minimal impact on mission effectiveness.
- **Worst Case**: Significant deterioration of security and humanitarian conditions in affected regions.
- **Most Likely**: Gradual adaptation to budget constraints with some operational compromises.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Donald Trump
– Louis Charbonneau
– Richard Gowan
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitical stability, humanitarian aid, international relations