UN Security Council to vote on crucial Gaza peace plan – Hurriyet Daily News
Published on: 2025-11-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: UN Security Council Vote on Gaza Peace Plan
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The strategic judgment is that the U.S.-backed peace plan for Gaza is unlikely to pass due to significant geopolitical opposition, particularly from Russia and China, and regional skepticism. The most supported hypothesis is that the U.S. plan will face substantial amendments or be overshadowed by a rival proposal. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Engage in diplomatic efforts to address concerns of key stakeholders to build broader consensus.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The U.S.-backed peace plan will pass with minimal amendments, leading to the deployment of an international stabilization force in Gaza.
Hypothesis 2: The U.S.-backed peace plan will face significant opposition, leading to either its rejection or substantial amendments, possibly in favor of a rival proposal by Russia.
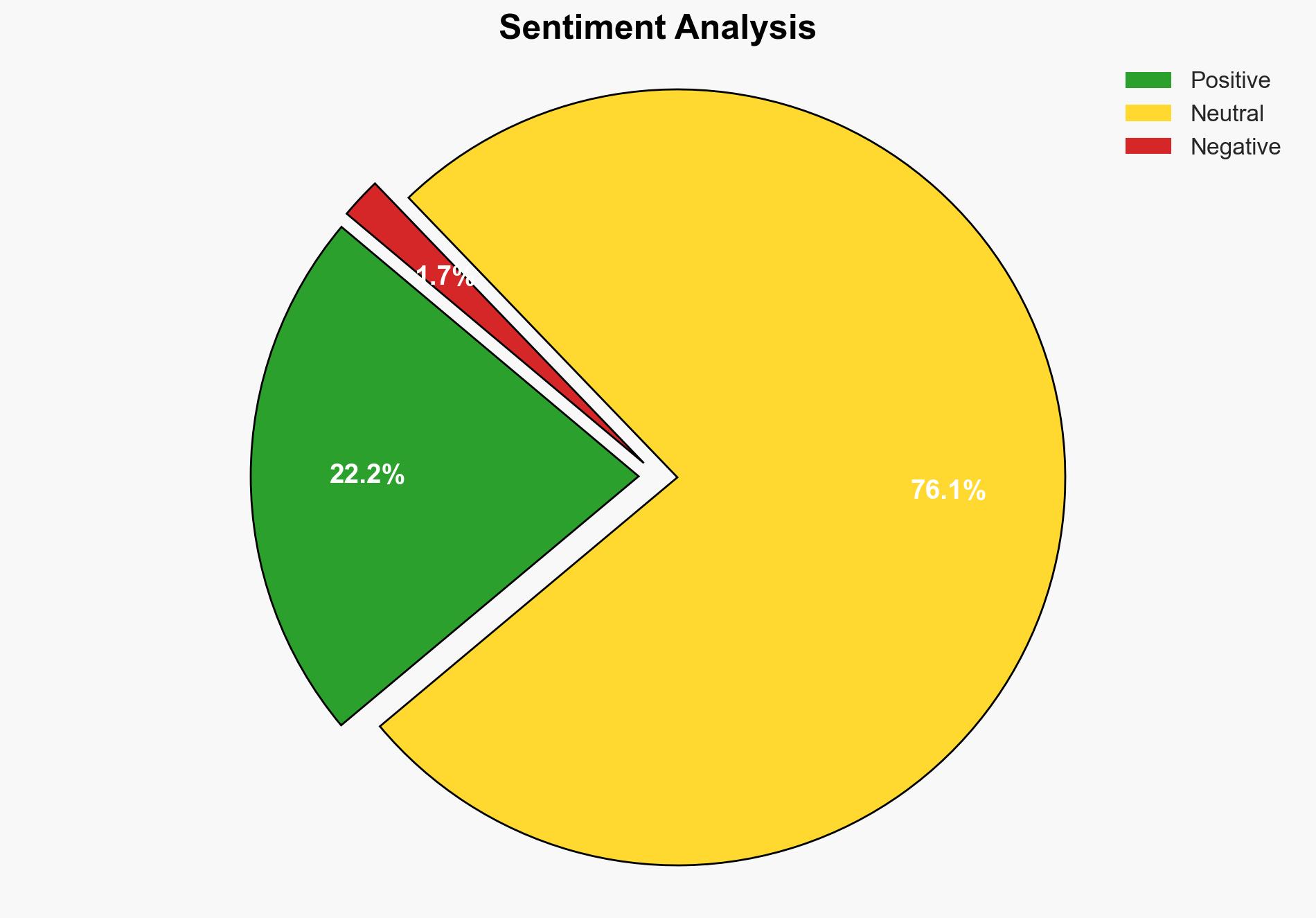
The second hypothesis is more likely due to the historical geopolitical dynamics at play, the existing opposition from Russia and China, and the regional skepticism from key Middle Eastern countries.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that international forces can stabilize Gaza without exacerbating tensions. A red flag is the potential for diplomatic rhetoric to mask underlying geopolitical maneuvers, particularly from Russia and China, who may use their influence to counter U.S. initiatives. Deception indicators include the possibility of states publicly supporting peace while privately undermining efforts to maintain regional influence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The failure to pass a consensus resolution could lead to increased instability in Gaza, with potential for escalated violence. Politically, the U.S. may face diminished influence in the region. Economically, continued instability could disrupt regional trade. Informationally, narratives around the legitimacy of international intervention could polarize global opinion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage in multilateral diplomacy to address concerns of Russia, China, and regional stakeholders.
- Prepare contingency plans for increased instability in Gaza if the resolution fails.
- Best-case scenario: A modified resolution passes, leading to a temporary stabilization of Gaza.
- Worst-case scenario: Resolution fails, leading to increased violence and geopolitical tension.
- Most-likely scenario: Resolution faces amendments, with a compromise reached that includes elements from both U.S. and Russian proposals.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Donald Trump, Gideon Saar, U.N. Security Council, Hamas, Palestinian Authority, Russia, China, Türkiye, Qatar, Egypt, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Jordan.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Middle East, Geopolitics, International Relations, Peacekeeping, U.N. Security Council
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·