United Nations to cut 25 of its global peacekeeping force in response to US funding strains – ABC News
Published on: 2025-10-09
Intelligence Report: United Nations to cut 25% of its global peacekeeping force in response to US funding strains – ABC News
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
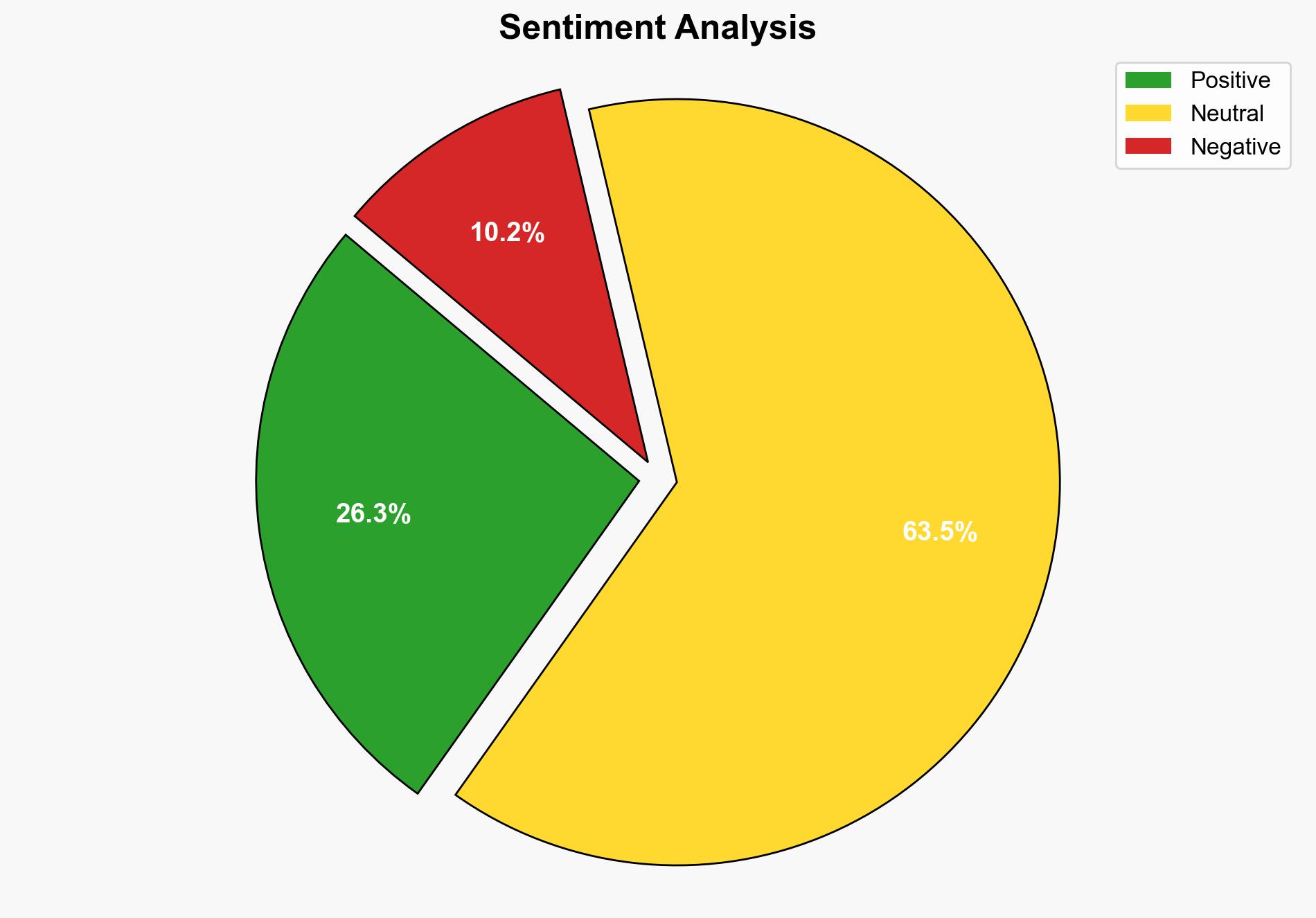
The United Nations’ decision to reduce its peacekeeping force by 25% is primarily driven by funding constraints, notably from the United States. The most supported hypothesis is that the cuts are a strategic realignment in response to reduced US contributions, reflecting broader geopolitical shifts. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Engage with key stakeholders to explore alternative funding mechanisms and assess the impact on global stability.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The reduction in the UN peacekeeping force is primarily a response to US funding cuts, reflecting a shift in US foreign policy under the Trump administration towards reduced multilateral engagement.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The reduction is part of a broader UN strategy to streamline operations and improve efficiency, independent of US funding changes, driven by internal assessments of peacekeeping effectiveness.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported due to direct references to US funding cuts and statements from US officials emphasizing budget constraints and a reevaluation of multilateral commitments.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Hypothesis A assumes that US funding is a critical factor in UN operations, and its reduction necessitates immediate operational changes. Hypothesis B assumes that the UN has independently identified inefficiencies in its peacekeeping operations.
– **Red Flags**: Lack of detailed financial data on other major contributors’ responses. Potential bias in US statements framing the cuts as necessary reforms.
– **Blind Spots**: The impact of cuts on specific regions and missions is not fully detailed, leaving potential gaps in understanding the operational consequences.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Geopolitical**: Reduced peacekeeping presence could destabilize regions reliant on UN forces, potentially leading to increased conflict and humanitarian crises.
– **Economic**: Countries hosting peacekeeping missions may face economic strain due to reduced international support.
– **Psychological**: Perception of declining international commitment could embolden non-state actors and undermine local confidence in peace processes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage with other major contributors like China to fill funding gaps and maintain mission effectiveness.
- Conduct a comprehensive review of peacekeeping missions to prioritize critical operations.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best: Alternative funding sources are secured, maintaining mission integrity.
- Worst: Significant mission withdrawals lead to regional instability and conflict escalation.
- Most Likely: Partial funding recovery with scaled-back operations in less critical areas.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Antonio Guterres
– Mike Waltz
– Donald Trump
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitical shifts, peacekeeping, multilateral funding challenges