US Forces Board Sanctioned Oil Tanker Linked to Venezuela Amid New Control Measures on Oil Distribution
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US forces board Venezuela-linked sanctioned oil tanker in North Atlantic US official says
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
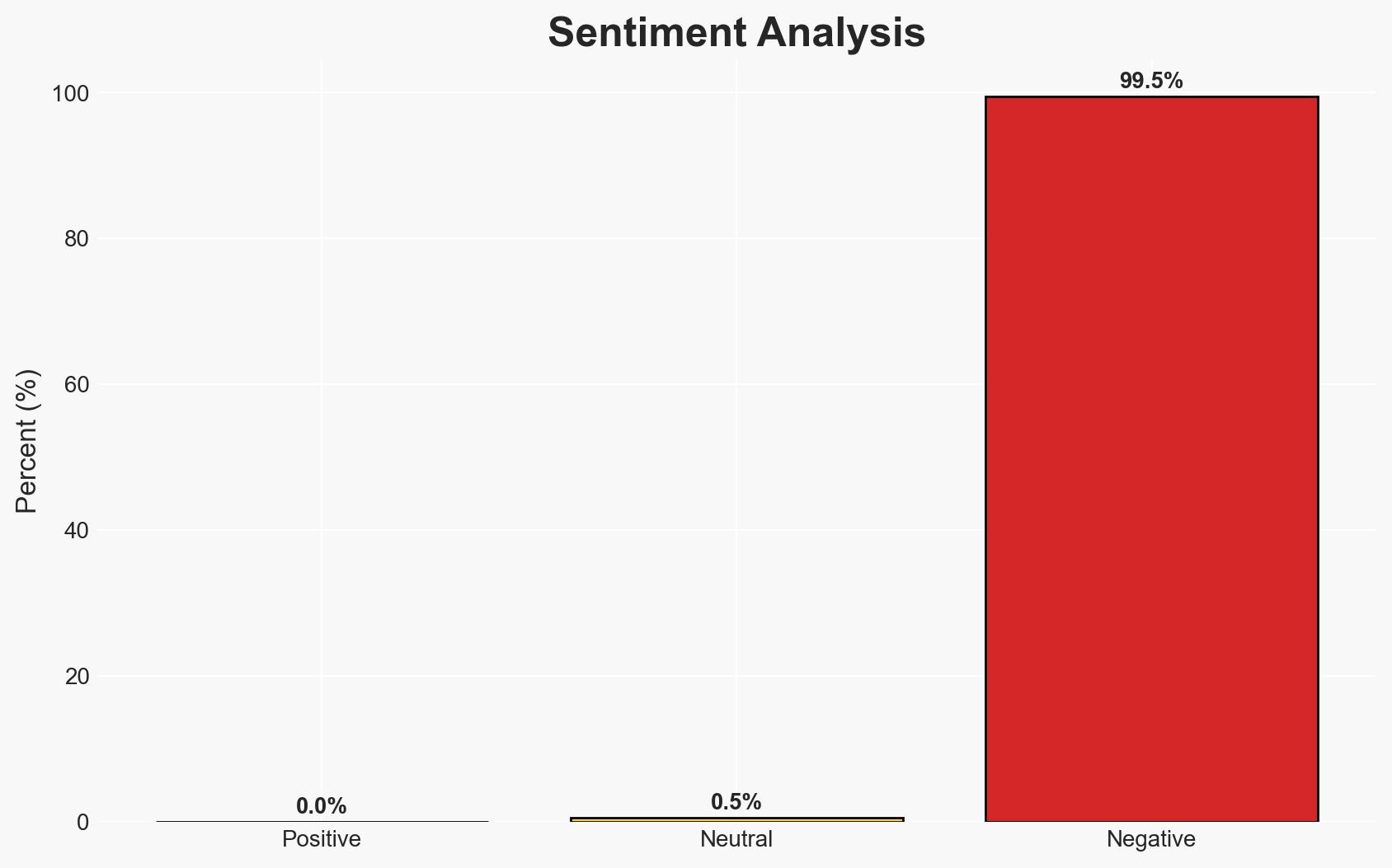
The U.S. has seized Venezuela-linked oil tankers in the North Atlantic, reflecting a strategic move to control Venezuelan oil distribution globally. This action is likely to impact U.S.-Venezuela relations and global oil markets. The most likely hypothesis is that the U.S. aims to leverage Venezuelan oil resources for geopolitical influence. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. is seizing Venezuelan oil tankers to exert control over global oil markets and influence oil prices. Supporting evidence includes the U.S. administration’s stated intention to control Venezuelan oil distribution. Key uncertainties include the long-term feasibility of such control and potential international backlash.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. actions are primarily aimed at destabilizing the Maduro regime by cutting off its revenue sources. This is supported by the context of existing sanctions and the U.S.’s historical stance against Maduro. Contradicting evidence includes the potential economic benefits to the U.S. from controlling oil sales.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit statements from U.S. officials about controlling oil distribution. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in U.S. policy or international responses to these actions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. has the capability to maintain control over Venezuelan oil exports; Venezuela lacks alternative revenue streams; international allies will support U.S. actions.
- Information Gaps: Details on the legal framework for U.S. control over Venezuelan oil; the response from other major oil-importing nations; the internal political situation in Venezuela.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in U.S. official statements aiming to justify actions; risk of Venezuelan or allied propaganda portraying the U.S. actions negatively.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, particularly with countries opposing U.S. sanctions. Over time, it may alter global oil supply dynamics and affect international relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for strained relations with countries reliant on Venezuelan oil; risk of retaliatory actions by Venezuela or its allies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of maritime confrontations; potential for asymmetric responses from affected parties.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting U.S. oil infrastructure; information warfare to shape narratives.
- Economic / Social: Impact on global oil prices; potential economic destabilization in Venezuela leading to increased migration pressures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor international reactions; assess legal implications of oil control; engage with allies to ensure support.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential retaliatory actions; strengthen partnerships with key oil-importing nations.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: U.S. successfully controls oil distribution with minimal backlash. Worst: Significant geopolitical tensions and economic disruptions. Most-Likely: U.S. faces moderate international criticism but maintains control.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- President Donald Trump
- Secretary of State Marco Rubio
- Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem
- U.S. European Command
- Venezuelan interim authorities
7. Thematic Tags
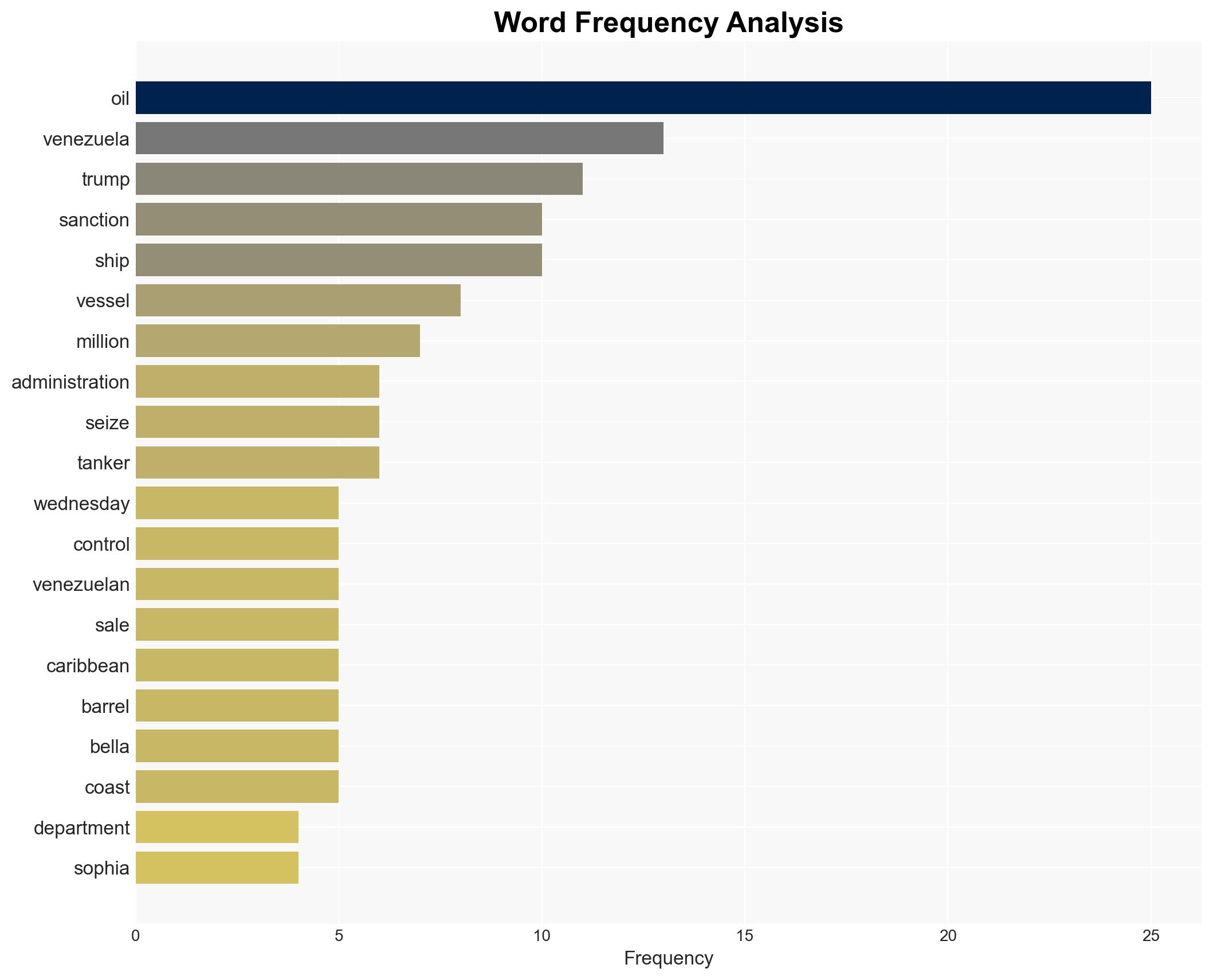
national security threats, sanctions, oil control, geopolitical strategy, U.S.-Venezuela relations, maritime security, economic impact, international law
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us