US Military Maneuvers in Middle East Highlight Limitations of Neoliberal Foreign Policy Amid Iran Crisis
Published on: 2026-02-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Iran Crisis Exposes the Impotence of Americas Neoliberal War Machine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
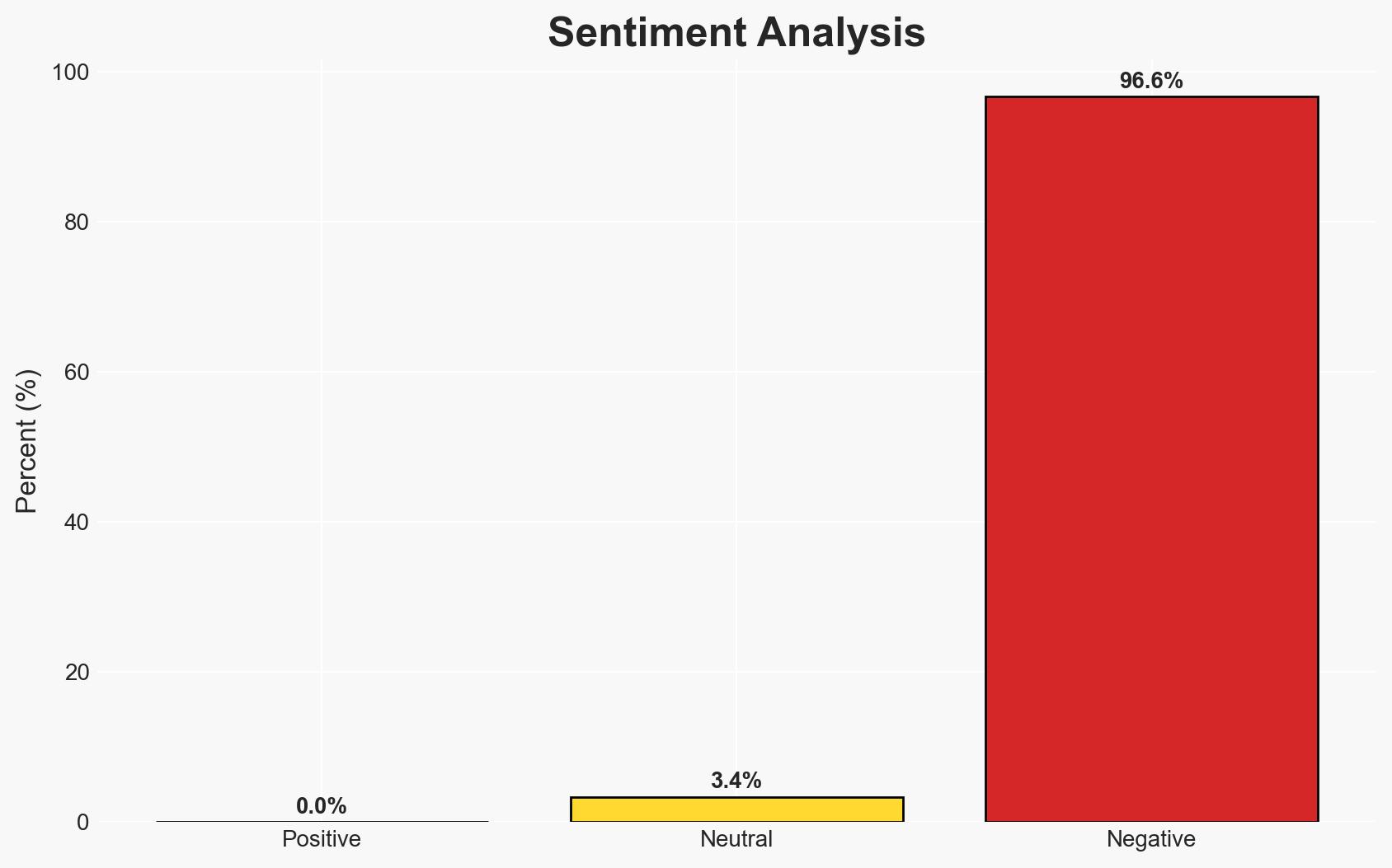
The United States is escalating its military posture in the Middle East by deploying additional naval assets, potentially setting the stage for increased tensions with Iran. This move could provoke significant Iranian retaliation, risking broader regional conflict. The situation is complicated by domestic political pressures in the U.S. and Iran’s strategic deterrence calculations. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. deployment is a strategic maneuver to deter further Iranian aggression and reassure regional allies. Supporting evidence includes the historical pattern of U.S. military presence as a deterrent. Contradicting evidence includes the potential for escalation rather than deterrence.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. is preparing for a potential military engagement with Iran, using the deployment as a pretext for action. Supporting evidence includes the extension of the carrier’s deployment and the rhetoric of potential military action. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of explicit public statements committing to military action.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the pattern of military deployments and the political context within the U.S. that may favor a show of strength. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in diplomatic engagements or public statements from U.S. leadership.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. deployment is primarily aimed at deterrence; Iran will respond proportionally to U.S. actions; U.S. domestic politics influence foreign policy decisions.
- Information Gaps: Details on U.S. strategic objectives in the region, Iranian military readiness and intentions, and the impact of U.S. domestic political dynamics on foreign policy.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting U.S. military movements as aggressive; Iranian statements may be strategic posturing rather than genuine intent.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased military tensions in the Middle East, affecting global energy markets and regional stability. The U.S. and Iran may enter a cycle of provocation and retaliation, with broader geopolitical ramifications.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for escalation into broader conflict involving regional and global powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to U.S. and allied forces in the region, potential for asymmetric warfare tactics by Iran.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likelihood of increased cyber operations targeting U.S. and Iranian infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Potential disruptions to global oil supply, impacting economic stability; heightened social tensions within Iran.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on Iranian military movements, increase diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions, and prepare contingency plans for rapid response.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances, develop resilience measures for potential cyber threats, and engage in multilateral forums to address underlying tensions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: De-escalation through diplomatic channels, leading to renewed negotiations.
- Worst: Full-scale military conflict with significant regional destabilization.
- Most-Likely: Continued military posturing with periodic skirmishes and diplomatic stalemates.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
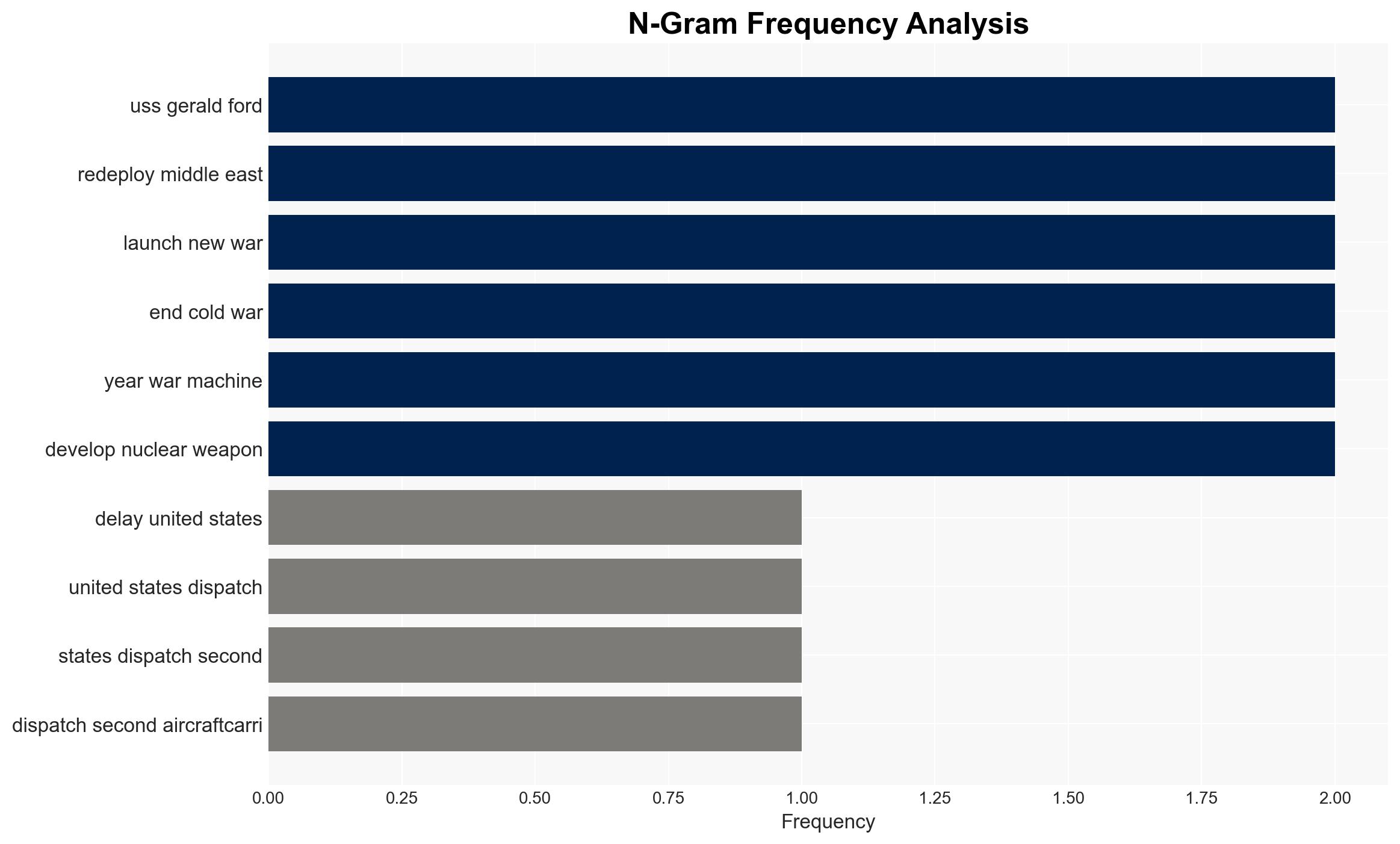
- President Donald Trump
- USS Gerald R. Ford
- USS Abraham Lincoln
- Iranian leadership (not specifically named)
- Foad Azadi, University of Tehran
7. Thematic Tags
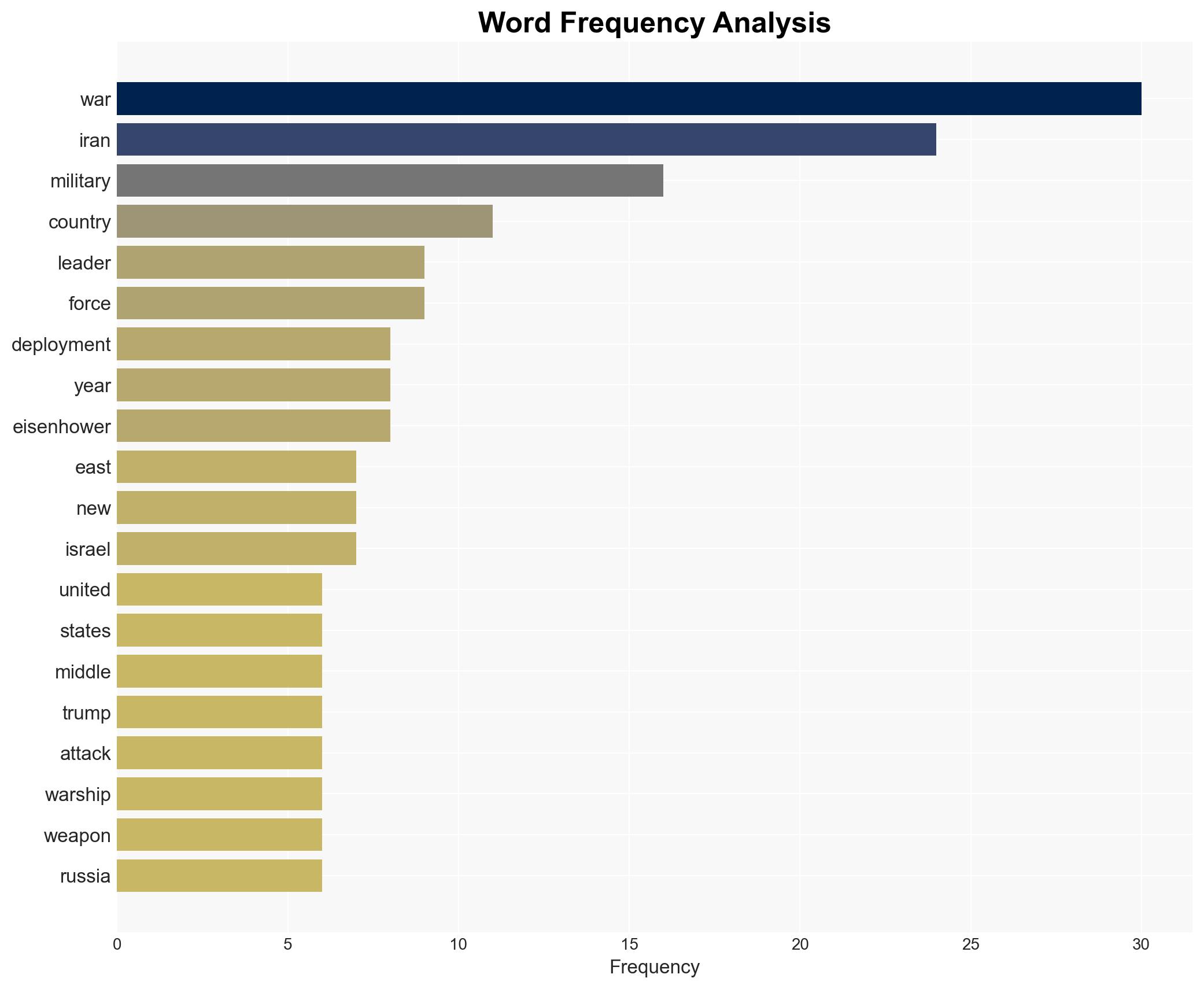
regional conflicts, military escalation, Middle East tensions, U.S. foreign policy, Iran deterrence, geopolitical risk, naval deployments, strategic deterrence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us