US military operations in Syria result in the death or capture of 25 ISIL fighters over nine days
Published on: 2025-12-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US says it killed or captured 25 ISIL operatives in Syria over nine days
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
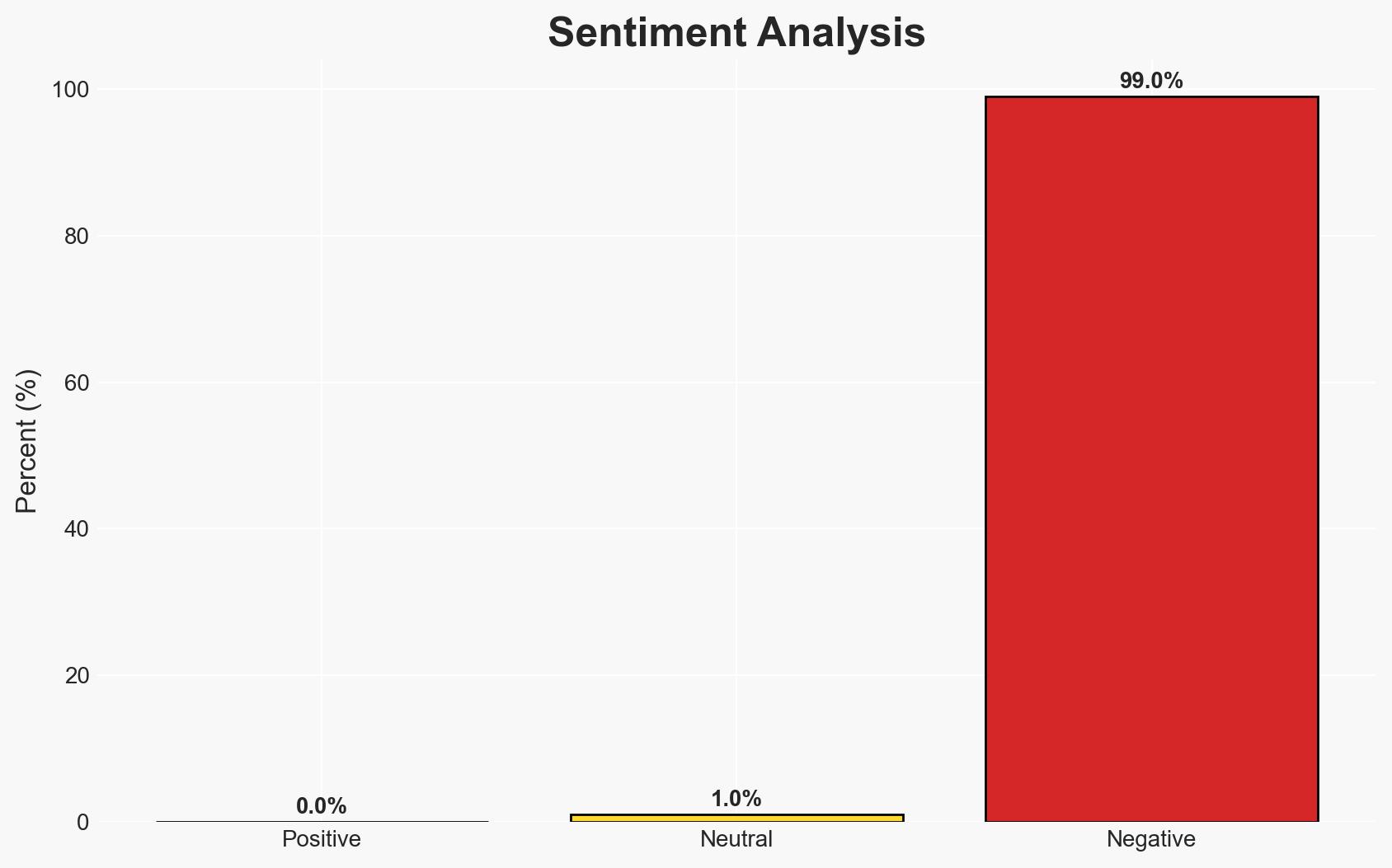
The US military’s recent operations in Syria resulted in the elimination or capture of 25 ISIL operatives, reflecting ongoing counter-terrorism efforts despite reduced troop presence. This activity suggests a continued threat from ISIL remnants in the region. The most likely hypothesis is that these operations are part of a broader strategy to prevent ISIL resurgence. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the identities of the operatives and the broader strategic context.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The operations are a direct response to recent ISIL attacks on US personnel, aimed at degrading ISIL’s operational capabilities. This is supported by the timing of the operations following the attack on US soldiers and the destruction of ISIL infrastructure. However, the lack of detailed information on the operatives’ identities limits full validation.
- Hypothesis B: The operations are part of a routine counter-terrorism strategy to maintain pressure on ISIL remnants, irrespective of recent attacks. This is supported by CENTCOM’s ongoing commitment to counter-terrorism in the region. Contradictory evidence includes the specific timing and intensity of the operations following the attack.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the temporal correlation between the ISIL attack on US forces and the subsequent operations. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include further details on the operatives’ roles and any changes in ISIL activity levels.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US military has accurate intelligence on ISIL operatives; ISIL remains a significant threat in Syria; US operations are primarily driven by recent attacks.
- Information Gaps: Identities and roles of the captured/killed operatives; ISIL’s current operational capabilities and strategic objectives.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on US military sources; risk of underestimating ISIL’s adaptive capabilities; possible misinformation from local partners.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a temporary reduction in ISIL activities in Syria but may also provoke retaliatory actions. The broader geopolitical dynamics, including US-Syria relations and regional stability, could be affected.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on US-Syria relations; impact on US alliances with regional partners like Jordan.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Short-term disruption of ISIL networks; potential for increased ISIL recruitment or propaganda efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in ISIL’s online propaganda to counter US narratives; risk of cyber retaliation.
- Economic / Social: Limited direct economic impact; potential social unrest if ISIL retaliates against local populations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence-sharing with regional partners; increase monitoring of ISIL communications and movements.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with local forces; invest in counter-radicalization programs; prepare for potential ISIL resurgence.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: ISIL’s operational capabilities are significantly degraded, leading to long-term regional stability.
- Worst: ISIL adapts and increases attacks, exploiting reduced US presence.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-level ISIL activity with periodic escalations, requiring sustained counter-terrorism efforts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- US Central Command (CENTCOM)
- ISIL (ISIS)
- Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF)
- President Ahmed al-Sharaa
- US President Donald Trump
- General Brad Cooper
7. Thematic Tags
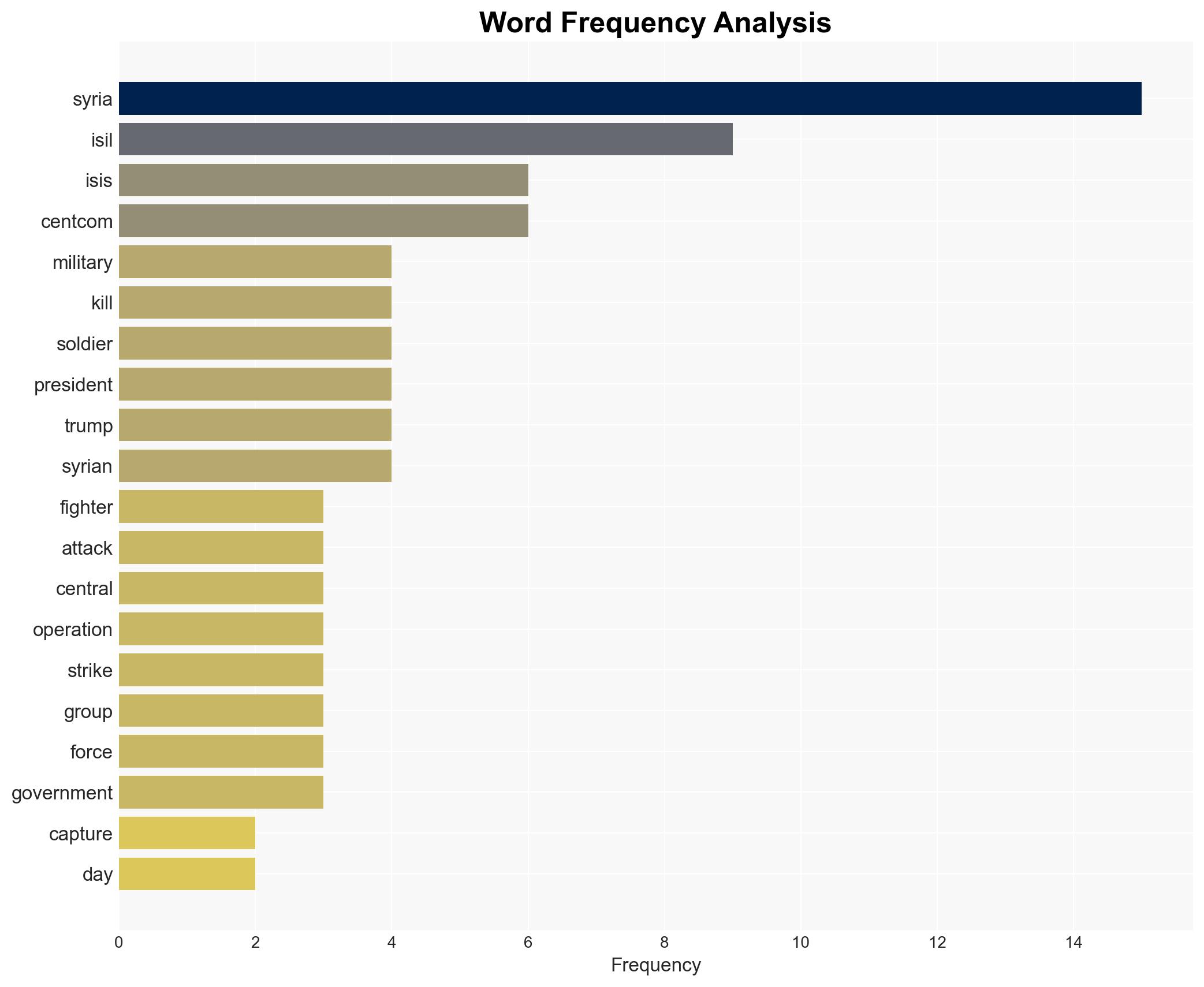
Counter-Terrorism, ISIL, US military operations, Syria, regional stability, intelligence sharing, geopolitical dynamics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us