US Warns Montenegro Over University’s Cooperation With Sanctioned Chinese Center – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-07-26
Intelligence Report: US Warns Montenegro Over University’s Cooperation With Sanctioned Chinese Center – Globalsecurity.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
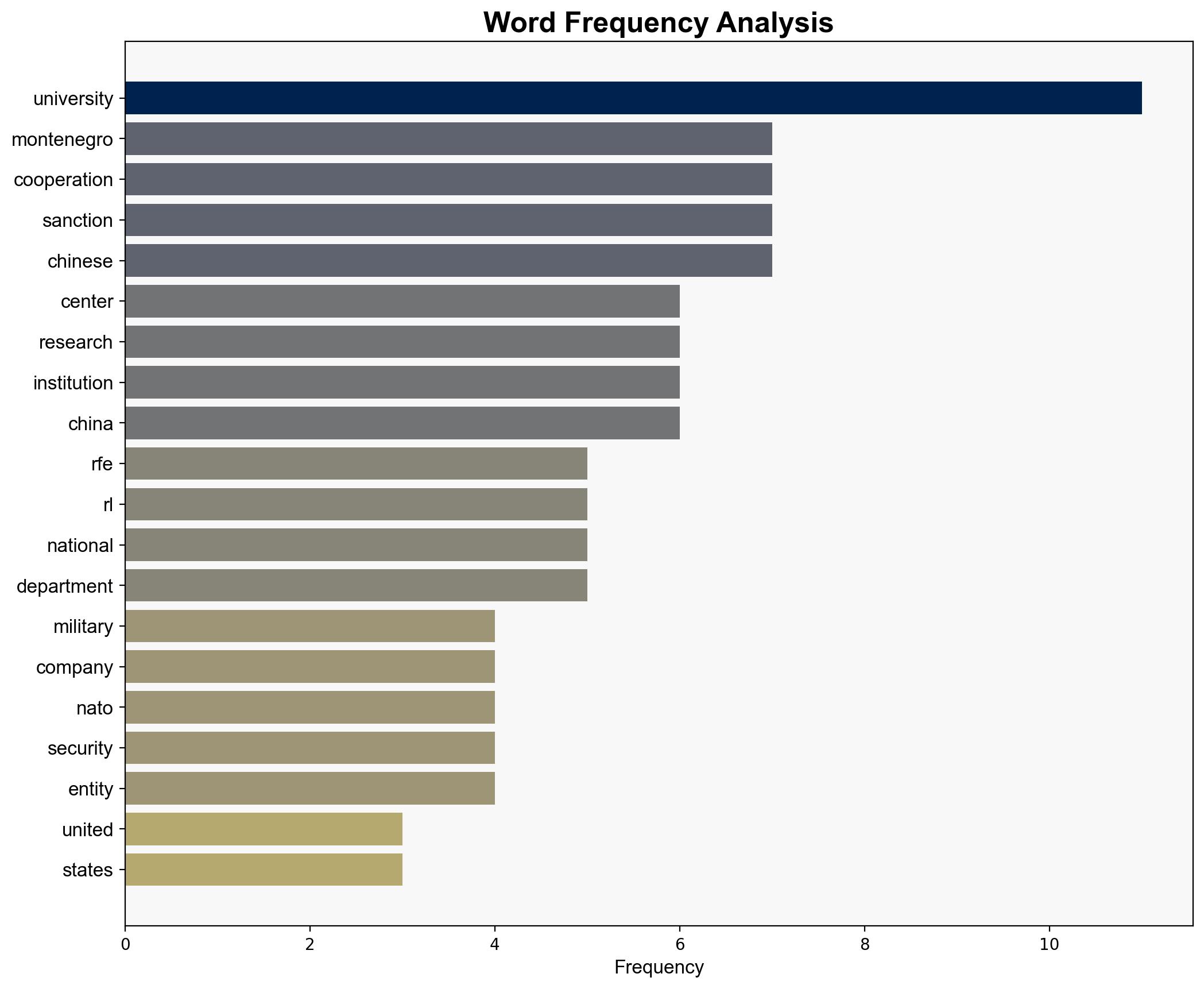
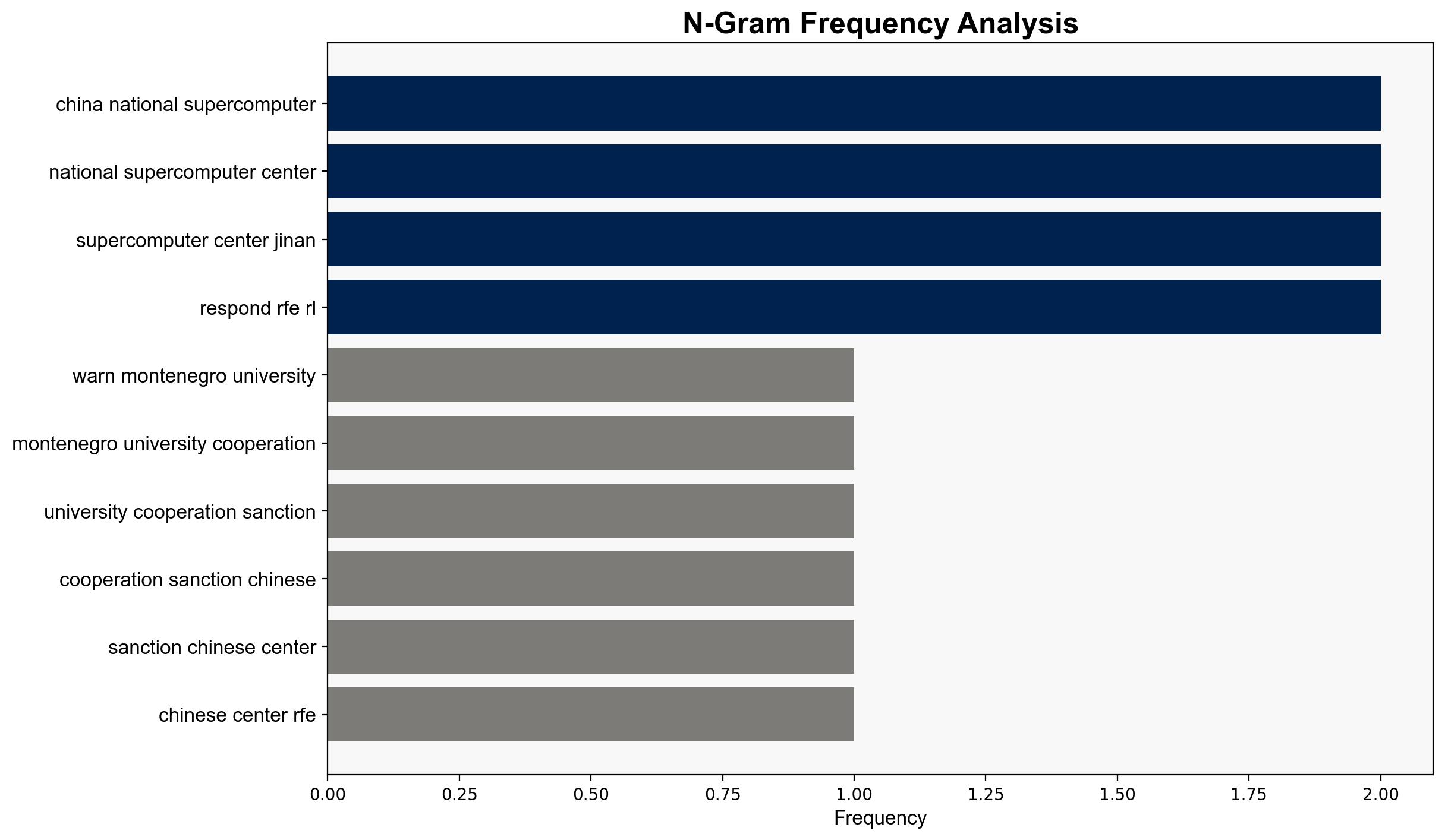
The most supported hypothesis is that the University of Montenegro’s cooperation with the Chinese National Supercomputer Center in Jinan poses a significant risk to NATO’s cybersecurity and strategic interests. This cooperation could inadvertently support China’s military modernization efforts. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Montenegro should reassess its partnerships and align them with NATO security priorities to mitigate potential risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis 1**: The University of Montenegro’s cooperation with the Chinese center is primarily academic, with no intent to support military objectives. This partnership aims to enhance Montenegro’s technological capabilities and academic standing.
2. **Hypothesis 2**: The cooperation is a strategic move by China to exploit Montenegro’s NATO membership and cyber capacity, potentially using the partnership as a backdoor for military and intelligence gains.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 2 is better supported due to the involvement of sanctioned entities and the strategic importance of the technologies involved (AI, cryptography, cybersecurity).
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the University of Montenegro is fully aware of the implications of cooperating with a sanctioned entity. There is also an assumption that the Chinese center’s intentions are aligned with China’s broader military objectives.
– **Red Flags**: The lack of transparency about the financial and human capital exchange between the university and the Chinese center. The involvement of entities like Hikvision, which are already blacklisted, raises concerns about compliance with international sanctions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Cybersecurity Risks**: Potential for compromised NATO cybersecurity infrastructure.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Strain on Montenegro’s relations with NATO allies, leading to possible diplomatic isolation.
– **Economic Risks**: Potential sanctions or economic penalties against Montenegro if it is perceived as undermining NATO security.
– **Escalation Scenarios**: Increased scrutiny from NATO could lead to heightened tensions with China, impacting regional stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Montenegro should conduct a thorough review of its international partnerships, ensuring alignment with NATO security protocols.
- Engage in dialogue with NATO allies to reaffirm commitment to shared security goals.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Montenegro realigns its partnerships, enhancing its cybersecurity posture and regional leadership.
- **Worst Case**: Continued cooperation leads to NATO sanctions, damaging Montenegro’s economy and international standing.
- **Most Likely**: Montenegro faces diplomatic pressure to sever ties, leading to a reevaluation of its international collaborations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Vladimir Bozovic
– University of Montenegro
– Chinese National Supercomputer Center in Jinan
– Hikvision
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus