USS Gerald R. Ford Carrier Deploys to Middle East Amid Heightened Tensions with Iran
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: USS Gerald R Ford aircraft carrier headed from Caribbean to Middle East Officials
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
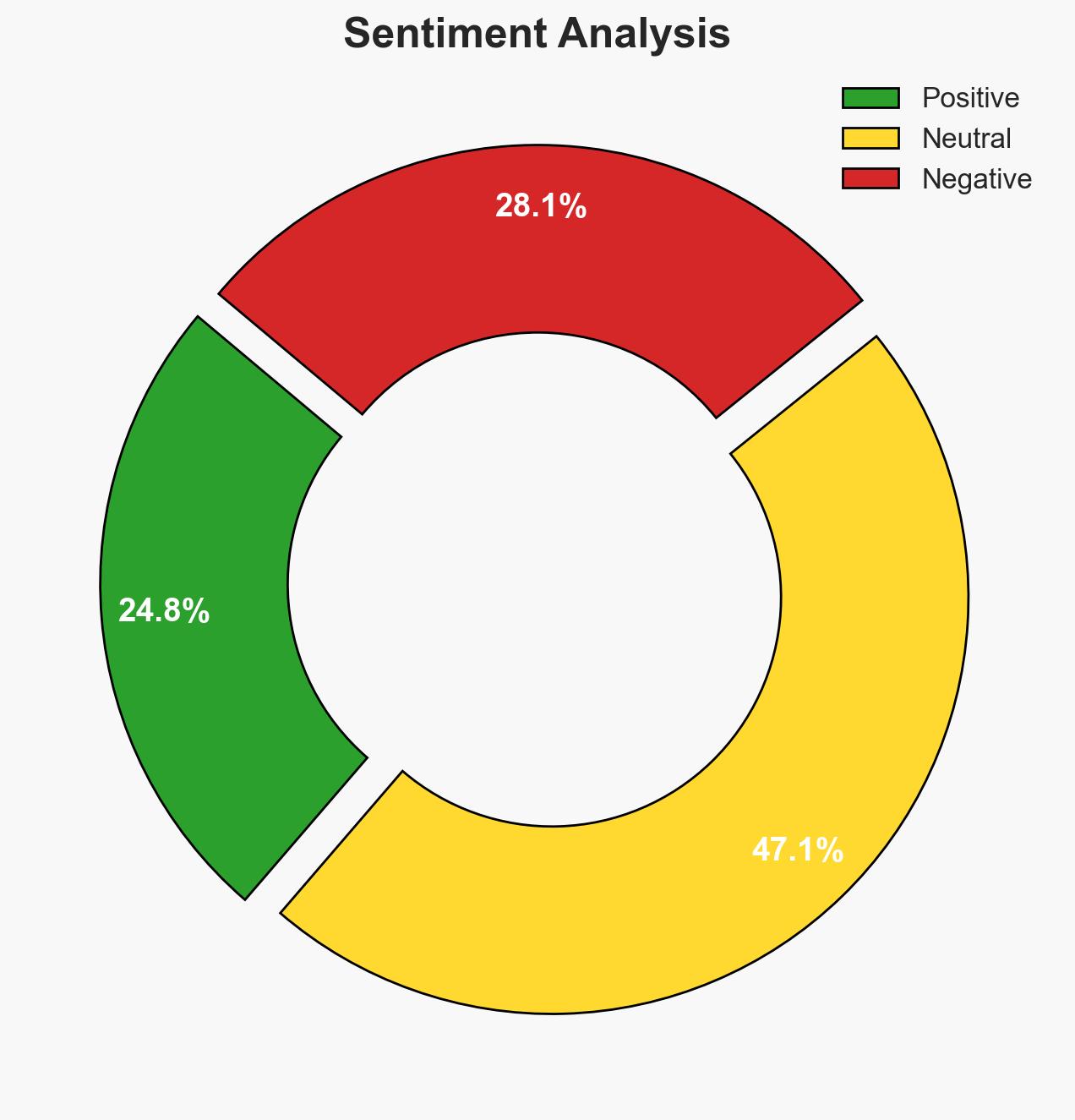
The USS Gerald R. Ford is being redeployed from the Caribbean to the Middle East as a strategic maneuver to pressure Iran amid ongoing nuclear negotiations. This move signals a potential escalation in U.S.-Iran tensions, with implications for regional stability. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the current geopolitical context and available information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The redeployment of the USS Gerald R. Ford is primarily a strategic pressure tactic by the U.S. to influence ongoing negotiations with Iran. Supporting evidence includes President Trump’s statements linking the deployment to negotiation outcomes. Key uncertainties include the actual impact on Iranian decision-making and the U.S.’s willingness to engage militarily.
- Hypothesis B: The redeployment is a precautionary measure in anticipation of potential military conflict with Iran, irrespective of negotiation outcomes. This is supported by the presence of another carrier in the region and Trump’s ambiguous statements about regime change. Contradicting evidence includes Trump’s expressed confidence in successful negotiations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit statements by U.S. officials linking the deployment to negotiation leverage. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Iranian military posture or U.S. rhetoric suggesting imminent conflict.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. is committed to diplomatic solutions; Iran perceives the carrier deployment as a credible threat; regional allies are aligned with U.S. actions; the carrier’s presence will not provoke unintended escalation.
- Information Gaps: Details on Iran’s internal decision-making processes; the specific timeline for U.S.-Iran negotiations; potential responses from regional actors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in interpreting U.S. intentions; source bias from U.S. officials emphasizing negotiation leverage; risk of Iranian misinformation campaigns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions in the Middle East, affecting regional alliances and global energy markets. The presence of two carriers may deter Iranian aggression but also risks escalating military engagements.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on U.S.-Iran relations and impacts on U.S. alliances with Gulf states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of military confrontations or proxy conflicts in the region.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting U.S. and allied interests by Iranian actors.
- Economic / Social: Fluctuations in global oil prices and potential impacts on regional economies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on Iranian military movements; engage in diplomatic outreach to regional allies; monitor cyber threat indicators.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional defense partnerships; develop contingency plans for potential conflict scenarios; invest in cyber defense capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful negotiations lead to de-escalation and improved U.S.-Iran relations.
- Worst: Breakdown in talks results in military conflict, destabilizing the region.
- Most-Likely: Prolonged negotiations with intermittent tensions and military posturing.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Donald Trump – U.S. President
- USS Gerald R. Ford – U.S. Navy aircraft carrier
- USS Abraham Lincoln – U.S. Navy aircraft carrier
- Iranian Government – Negotiating counterpart
- U.S. Southern Command – Regional military command
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, military strategy, U.S.-Iran relations, nuclear negotiations, Middle East security, geopolitical tensions, naval deployments, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us