Venezuelan Leader Nicolás Maduro and Wife Charged with Drug and Weapons Offenses After U.S. Military Capture
Published on: 2026-01-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro Indicted on Drug Weapons Charges
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
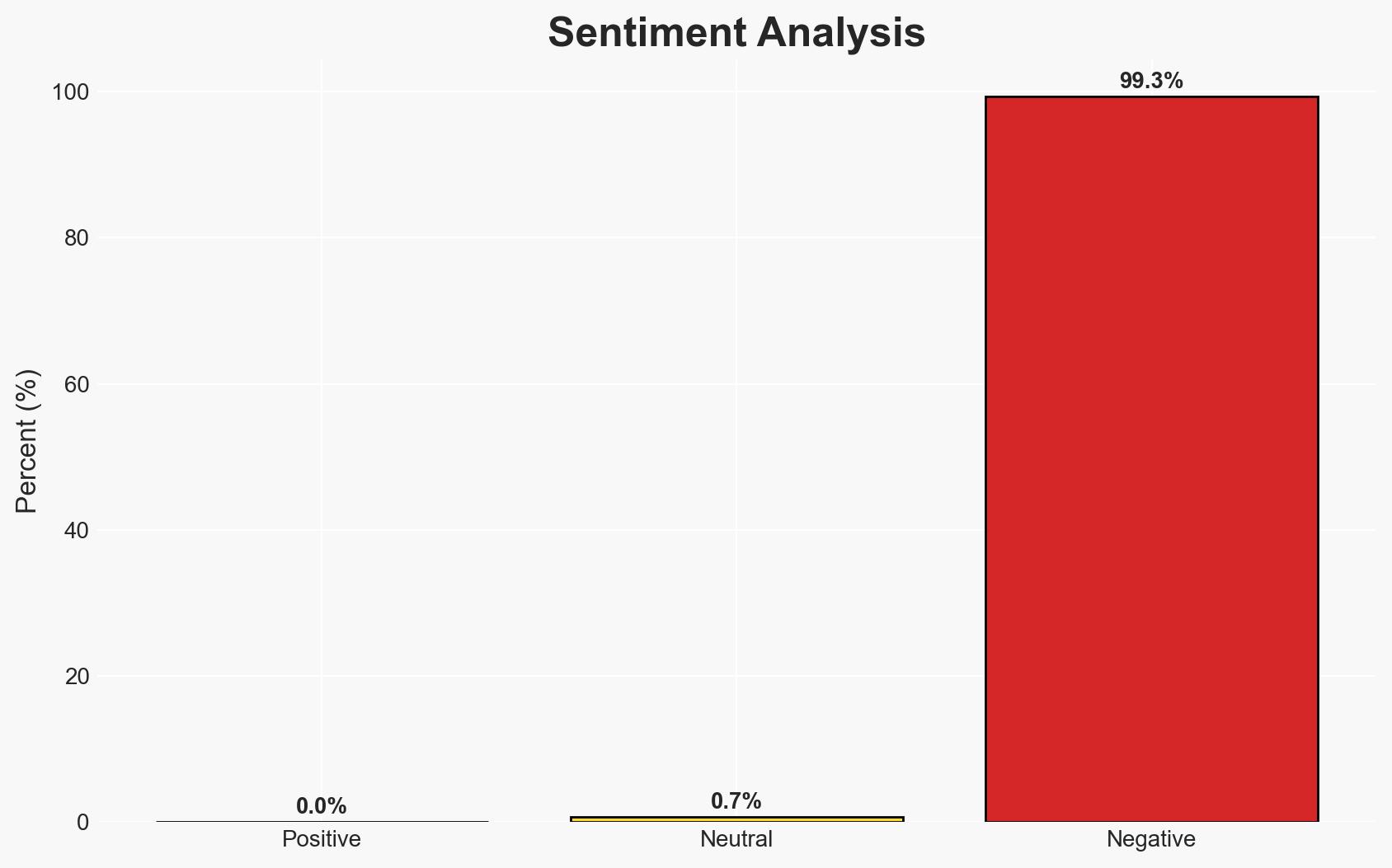
The United States has indicted Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro on drug and weapons charges following his capture by U.S. military forces. This development significantly alters the political landscape in Venezuela, with Vice President Delcy Rodríguez assuming the presidency under U.S. oversight. The situation presents potential geopolitical and economic ramifications, particularly concerning Venezuela’s oil reserves. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the U.S. strategy for managing Venezuela.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. military intervention and indictment of Maduro are primarily driven by a strategic interest in Venezuela’s oil reserves. Supporting evidence includes President Trump’s statements about American oil companies rebuilding Venezuela’s energy infrastructure. Contradicting evidence is the lack of clear U.S. policy details on managing Venezuela post-capture.
- Hypothesis B: The primary motivation for the U.S. action is to dismantle a narco-terrorism network allegedly led by Maduro. This is supported by the indictment’s focus on drug and weapons charges. However, the geopolitical focus on oil suggests additional motives.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit statements regarding oil interests. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include further U.S. policy clarifications or international responses emphasizing counter-narcotics over economic interests.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. has the capability and intent to manage Venezuelan governance effectively; Delcy Rodríguez will cooperate with U.S. directives; Venezuela’s military will not resist U.S. actions.
- Information Gaps: Detailed U.S. plans for Venezuela’s governance; the reaction of Venezuelan military and civilian populations; international community’s stance on U.S. intervention.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential U.S. political bias in framing the intervention; Venezuelan state media may manipulate narratives to incite anti-U.S. sentiment.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This intervention could destabilize Venezuela, impacting regional stability and U.S. relations with Latin American countries. It may also set a precedent for U.S. military involvement in foreign governance under the guise of counter-narcotics operations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between the U.S. and countries opposing foreign intervention; risk of civil unrest in Venezuela.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible escalation of violence from Maduro loyalists or allied groups; increased U.S. military presence in the region.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likelihood of disinformation campaigns from both U.S. and Venezuelan sources to control narratives.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in oil markets; potential humanitarian crisis if governance transition is mismanaged.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Venezuelan military movements; engage with international partners to build consensus on intervention legitimacy; prepare for potential humanitarian aid deployment.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop a comprehensive strategy for Venezuela’s political transition; strengthen regional alliances to mitigate backlash; invest in intelligence capabilities to monitor internal Venezuelan dynamics.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Smooth transition of power with international support, leading to stabilization.
- Worst Case: Prolonged conflict with significant regional instability and humanitarian issues.
- Most Likely: Gradual transition with intermittent unrest and international diplomatic challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
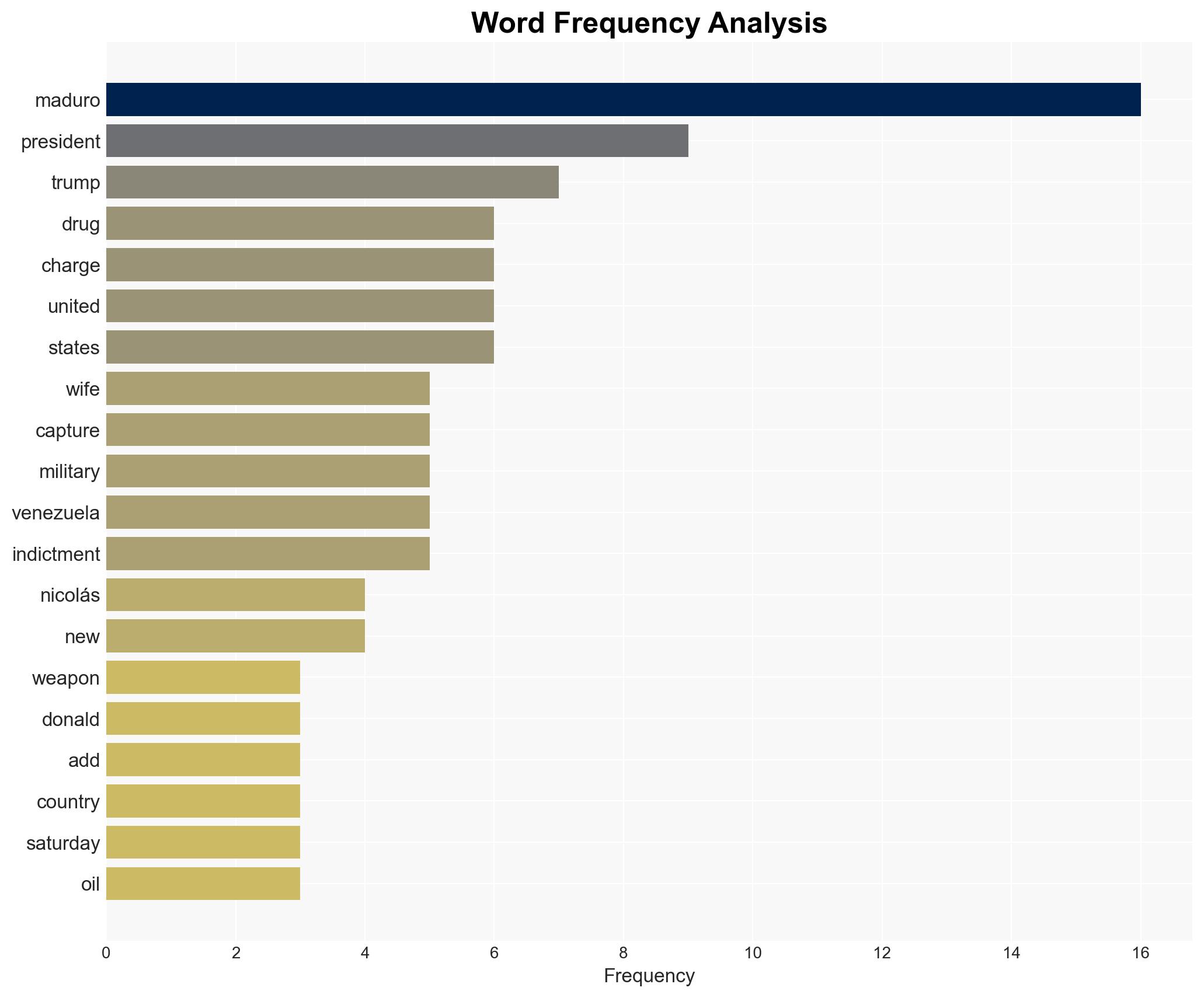
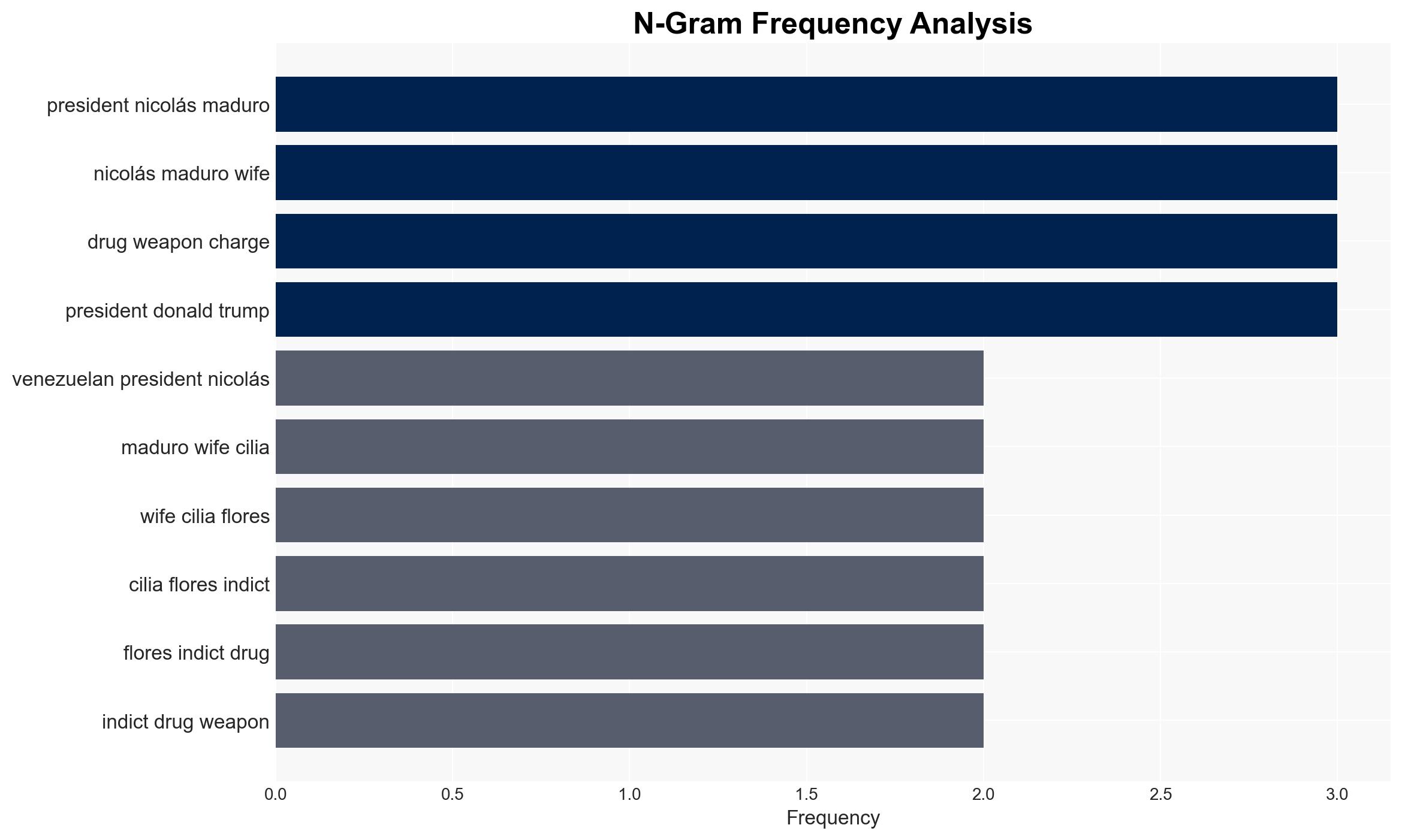
- Nicolás Maduro – Former President of Venezuela
- Cilia Flores – Wife of Nicolás Maduro
- Delcy Rodríguez – Vice President, now acting President of Venezuela
- Diosdado Cabello Rondon – Minister of the Interior
- Nicolás Ernesto Maduro Guerra – Son of Nicolás Maduro
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitics, narco-terrorism, U.S. foreign policy, oil reserves, military intervention, regime change, international law
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us