Vietnam ends death penalty for crimes against the state bribery drugs – Al Jazeera English
Published on: 2025-06-25
Intelligence Report: Vietnam Ends Death Penalty for Crimes Against the State, Bribery, and Drugs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
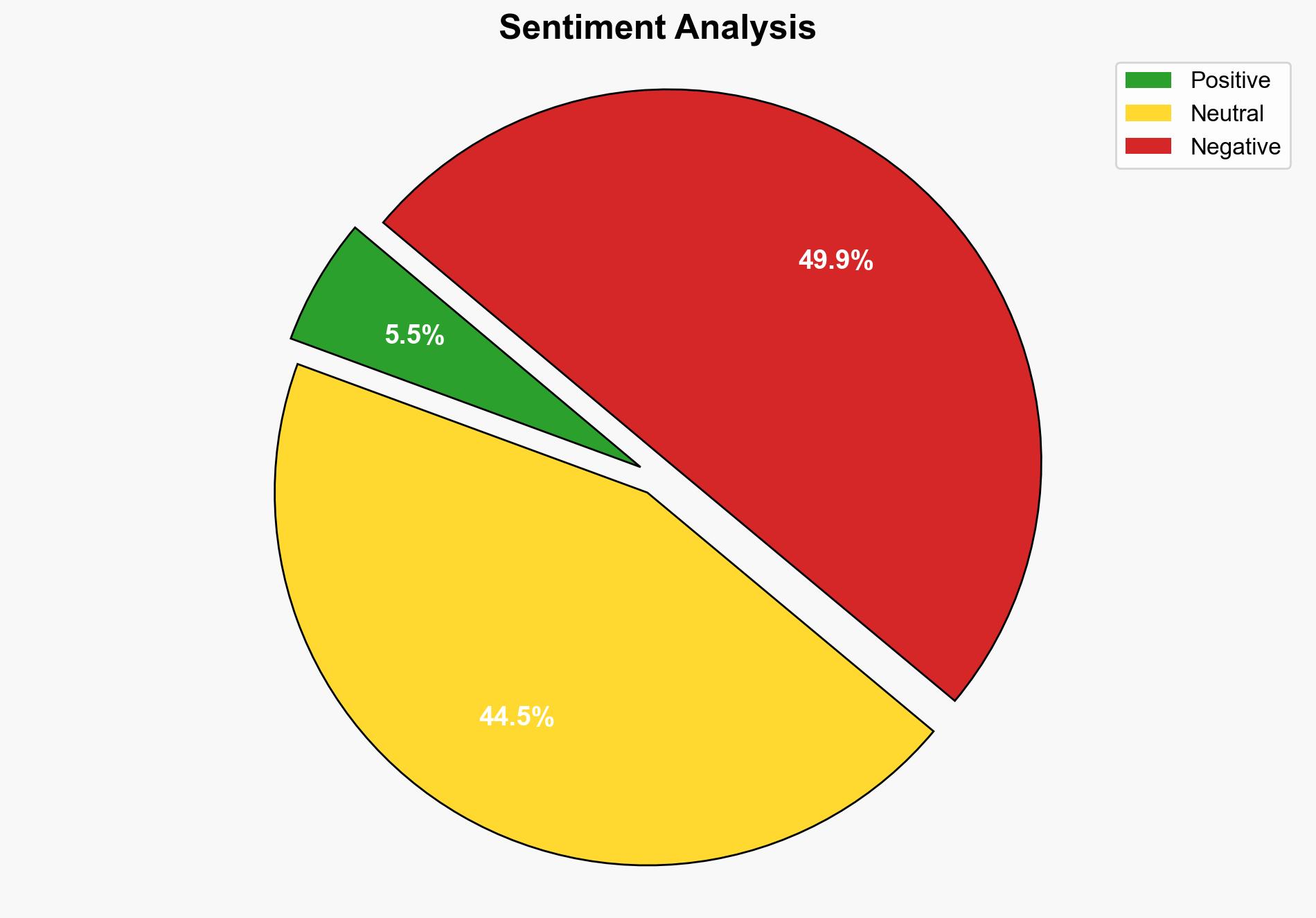
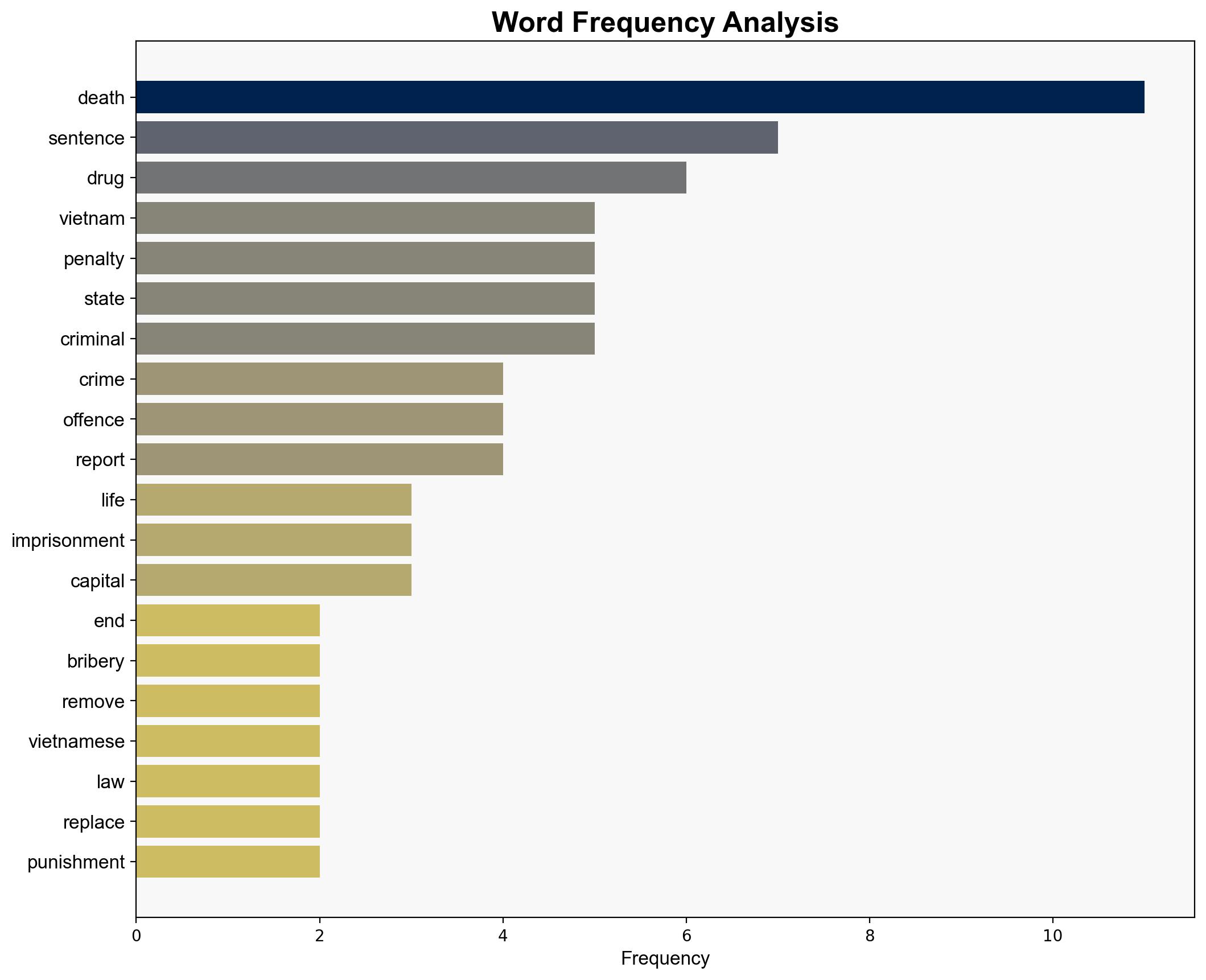
Vietnam’s decision to abolish the death penalty for crimes such as bribery, drug offenses, and crimes against the state marks a significant shift in its legal framework. This move could impact internal stability and international relations, potentially influencing regional security dynamics. Recommendations include monitoring the implementation of these changes and assessing their effects on crime rates and judicial processes.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied to ensure methodological consistency:
Cognitive Bias Stress Test
Potential biases in assessing Vietnam’s legal reforms have been addressed through structured challenge, ensuring a balanced view of the implications.
Bayesian Scenario Modeling
Probabilistic forecasting suggests a moderate likelihood of reduced execution rates leading to shifts in Vietnam’s international human rights standing.
Network Influence Mapping
Influence mapping highlights potential shifts in power dynamics within Vietnam’s political and judicial systems, as well as impacts on regional actors.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The abolition of the death penalty for specific crimes may lead to changes in crime patterns, with potential increases in certain offenses if deterrence is perceived as weakened. Regionally, this could alter Vietnam’s diplomatic relations, particularly with countries advocating for human rights reforms. The shift may also affect internal political stability, depending on public and political reactions.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor crime statistics and judicial outcomes to assess the impact of the legal changes.
- Engage with regional partners to understand broader implications for Southeast Asian security dynamics.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Enhanced international reputation and improved human rights record.
- Worst Case: Increased crime rates and internal dissent.
- Most Likely: Gradual adaptation with mixed outcomes on crime and international relations.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The Vietnamese National Assembly, which played a crucial role in passing the amendments to the criminal code.
6. Thematic Tags
legal reform, human rights, regional security, judicial processes