Warlock Ransomware Exploits Unpatched SmarterMail Server in SmarterTools Network Breach
Published on: 2026-02-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Warlock Ransomware Breaches SmarterTools Through Unpatched SmarterMail Server
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
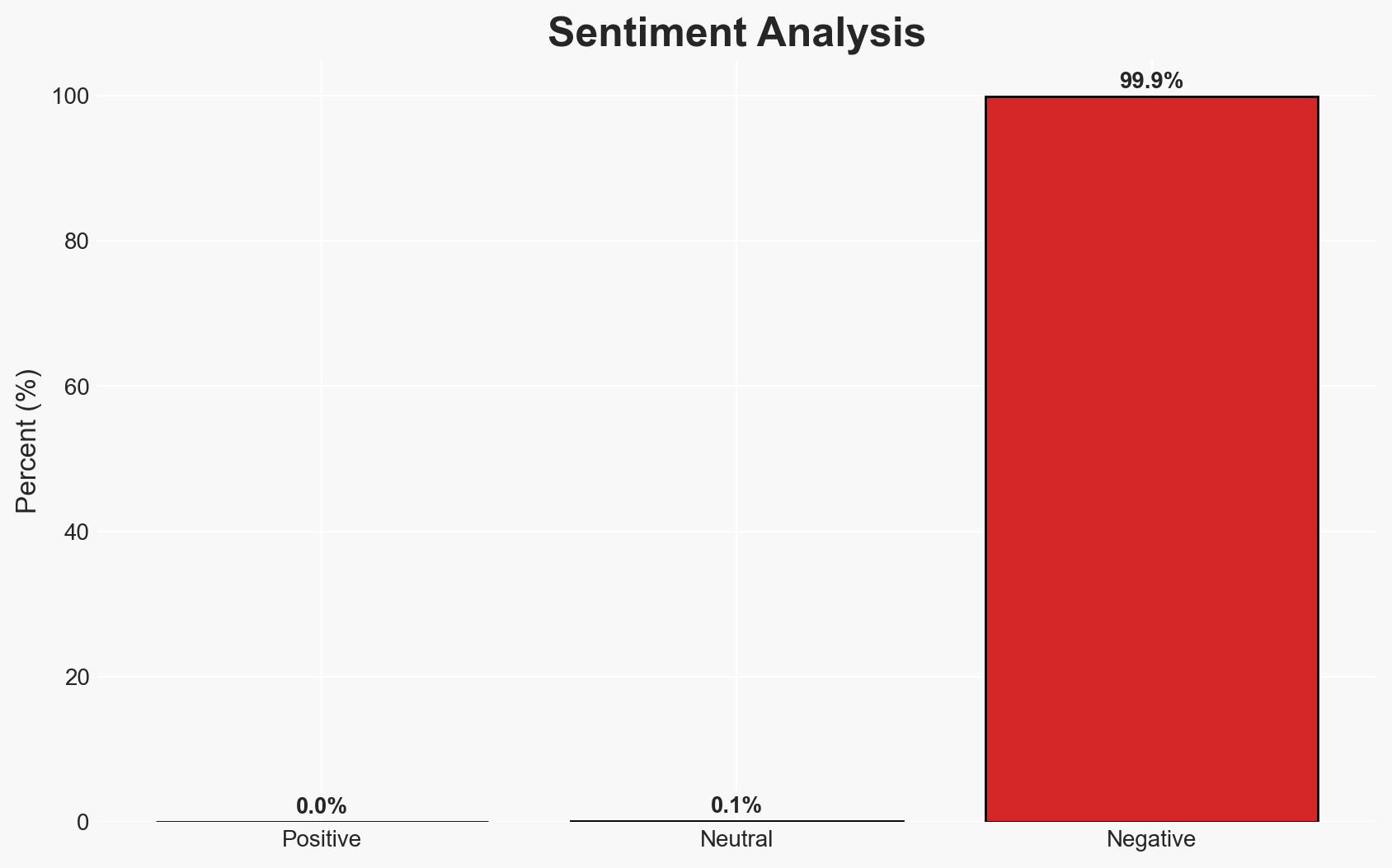
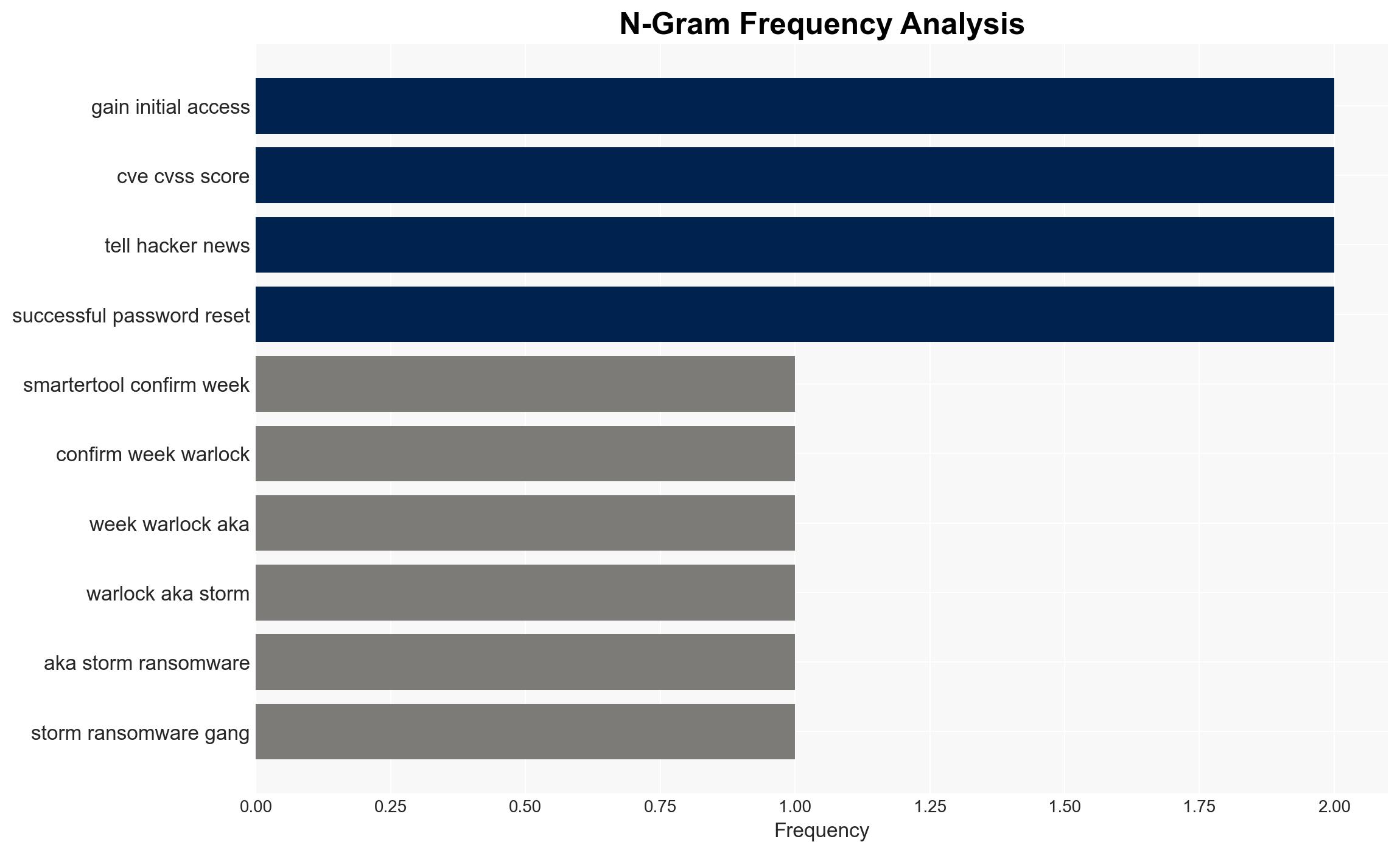
The Warlock ransomware group successfully breached SmarterTools by exploiting an unpatched SmarterMail server, impacting several internal systems and hosted customer environments. The breach highlights significant vulnerabilities in SmarterTools’ network management and patching processes. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to limited information on the specific vulnerability exploited and the full extent of the breach.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily due to a failure in SmarterTools’ internal patch management processes, allowing exploitation of a known vulnerability. This is supported by the admission of an unpatched server and the existence of known vulnerabilities. However, the specific vulnerability exploited remains unidentified, creating uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was facilitated by insider negligence or potential insider threat, given the unawareness of the unpatched VM. While plausible, there is no direct evidence of malicious insider activity, making this hypothesis less supported.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit acknowledgment of an unpatched system and known vulnerabilities. Indicators such as further internal audits or discovery of insider involvement could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: SmarterTools’ network management practices were inadequate; Warlock group had prior knowledge of the vulnerabilities; no critical data was compromised.
- Information Gaps: Specific vulnerability exploited; full scope of data accessed; potential insider involvement.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in SmarterTools’ public statements to minimize reputational damage; lack of independent verification of breach details.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach could encourage similar attacks on organizations with lax patch management, potentially escalating into broader cybersecurity threats. The incident underscores the need for robust cybersecurity practices and could influence regulatory scrutiny.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tension between nations over cybersecurity standards and responsibilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure and private sector entities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage and exploitation of similar vulnerabilities in other systems.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected companies and erosion of trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of all systems for unpatched vulnerabilities; enhance monitoring for signs of further breaches.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop and implement a rigorous patch management policy; establish partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patching and improved security measures prevent further incidents.
- Worst: Continued exploitation of vulnerabilities leads to significant data breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity posture reduce but do not eliminate risk.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Derek Curtis, Chief Commercial Officer, SmarterTools
- Tim Uzzanti, CEO, SmarterTools
- Warlock (aka Storm-2603) ransomware group
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other individuals/entities.
7. Thematic Tags
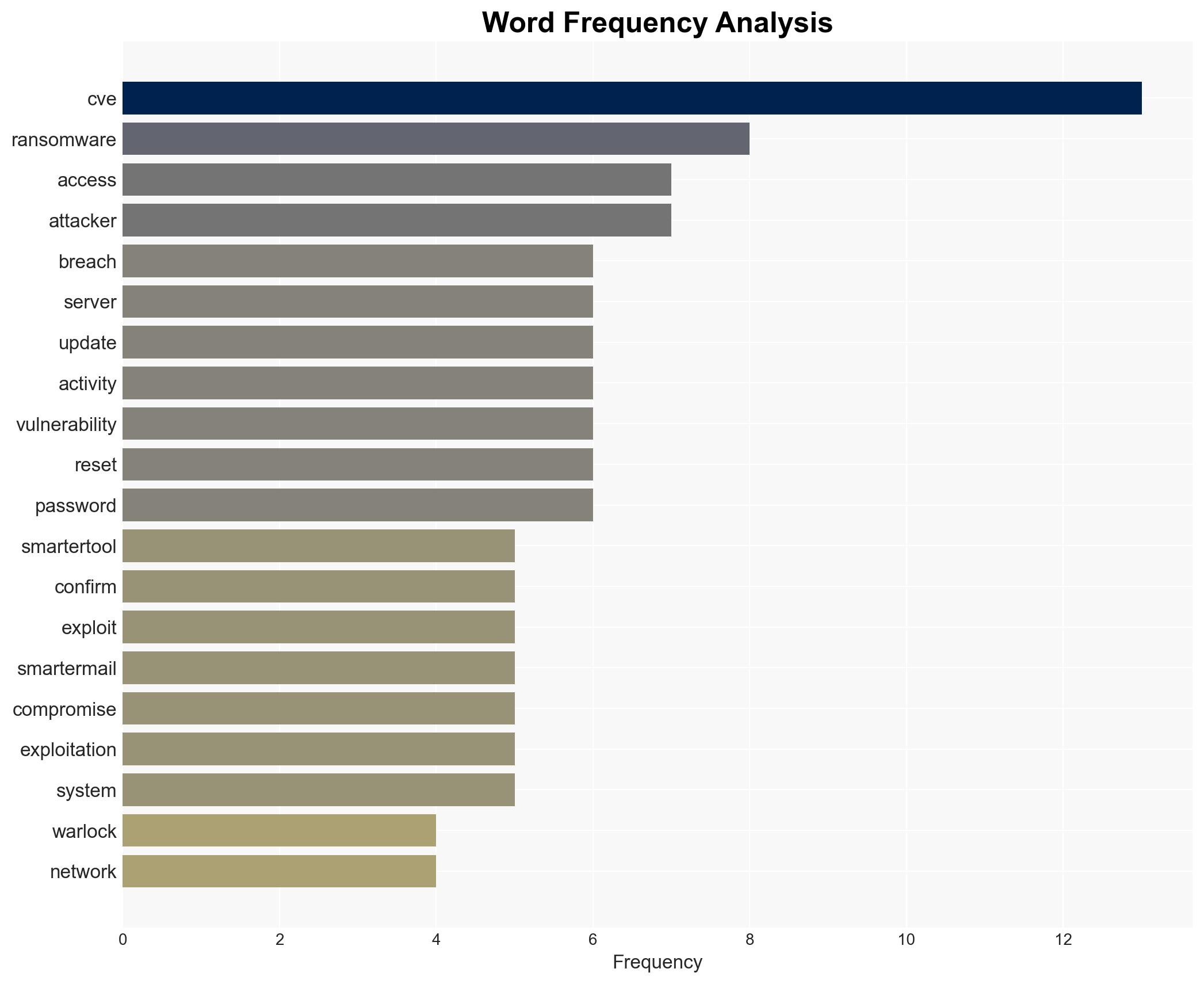
cybersecurity, ransomware, patch management, insider threat, SmarterTools, Warlock group, vulnerability exploitation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us