We should migrate now to post-quantum encryption researcher says – Cointelegraph
Published on: 2025-11-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: We should migrate now to post-quantum encryption researcher says – Cointelegraph
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
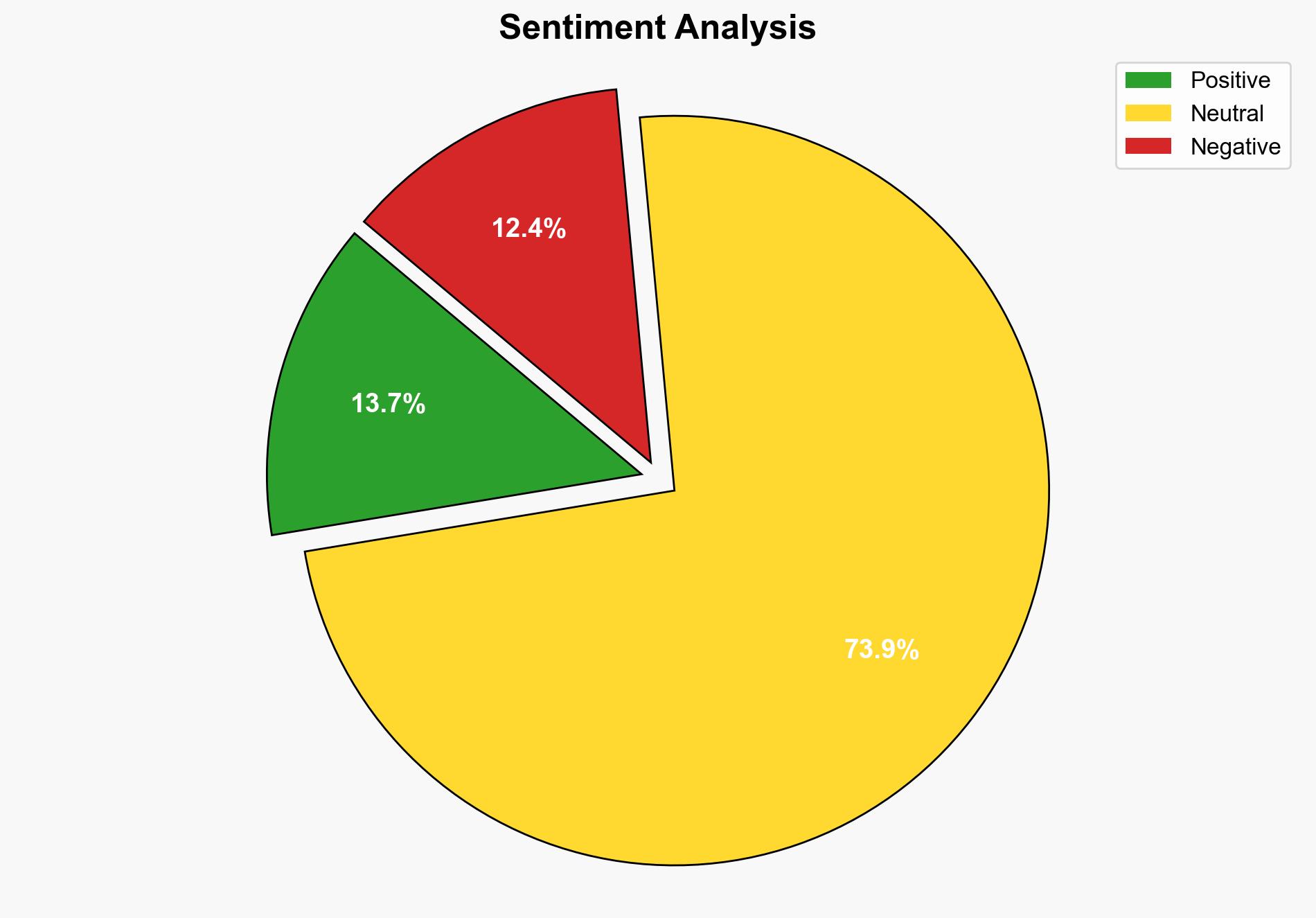
With a moderate confidence level, it is assessed that the transition to post-quantum encryption is a strategic necessity to preemptively counter potential threats from quantum computing advancements. Immediate investment in research and development of post-quantum cryptographic standards is recommended to mitigate future risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Quantum computing will advance rapidly, posing a significant threat to current encryption standards within the next decade. This hypothesis is supported by the potential for “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks and the strategic interest of state actors like China in developing quantum capabilities.
Hypothesis 2: The development of practical quantum computing is overestimated, and current encryption standards will remain secure for the foreseeable future. This hypothesis is supported by the current lack of commercial quantum computing and the complexity involved in developing quantum systems.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the strategic interests and investments by major tech companies and state actors in quantum computing, despite the uncertainty in the timeline of its development.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that quantum computing will eventually reach a stage where it can break current encryption standards. It is also assumed that state actors are actively pursuing quantum capabilities.
Red Flags: The potential for “quantum washing” where companies make dubious claims about their quantum capabilities. The lack of significant investment in post-quantum cryptography could slow down necessary advancements.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary risk is the potential for a significant cybersecurity threat if quantum computing advances faster than anticipated, leading to the compromise of encrypted data. This could have cascading effects on political, economic, and informational security globally. The risk of state actors gaining a strategic advantage through quantum capabilities could lead to geopolitical instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Invest in research and development of post-quantum cryptographic standards to ensure readiness against future quantum threats.
- Encourage collaboration between governments, academia, and industry to accelerate the development of secure post-quantum encryption methods.
- Monitor advancements in quantum computing and adjust cybersecurity strategies accordingly.
- Best-case scenario: Post-quantum encryption standards are developed and implemented before quantum computing becomes a threat.
- Worst-case scenario: Quantum computing advances rapidly, compromising current encryption standards and leading to widespread data breaches.
- Most-likely scenario: Gradual advancements in quantum computing with sufficient time to develop and implement post-quantum encryption standards.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Gianluca Di Bella, a smart contract researcher specializing in zero-knowledge proof and quantum computing threats. Notable entities include Microsoft, Google, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Quantum Computing, Cryptography, Strategic Risk
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology