Weak alerting and slipping prevention raise risk levels for CISOs – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-08-18
Intelligence Report: Weak alerting and slipping prevention raise risk levels for CISOs – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
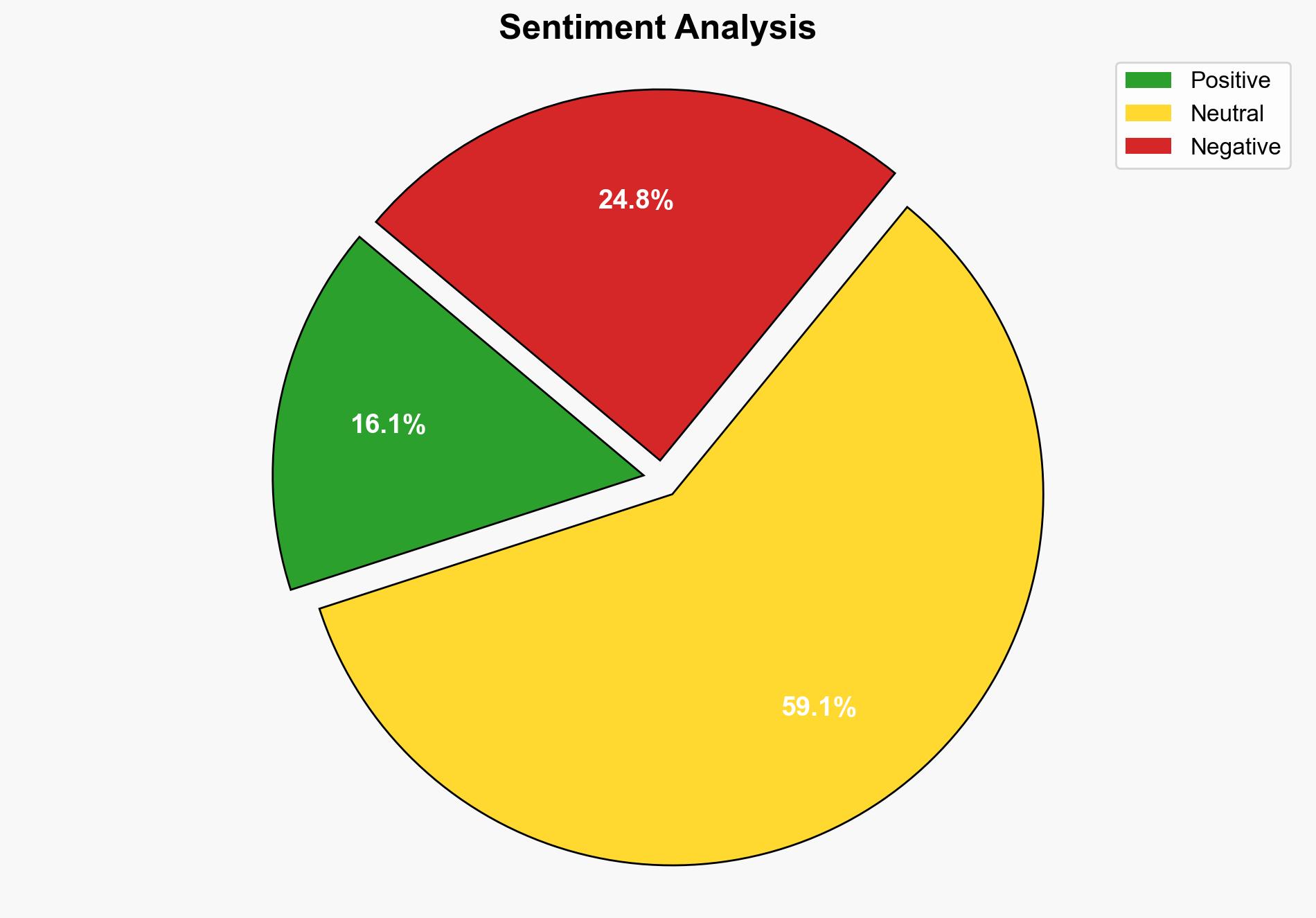
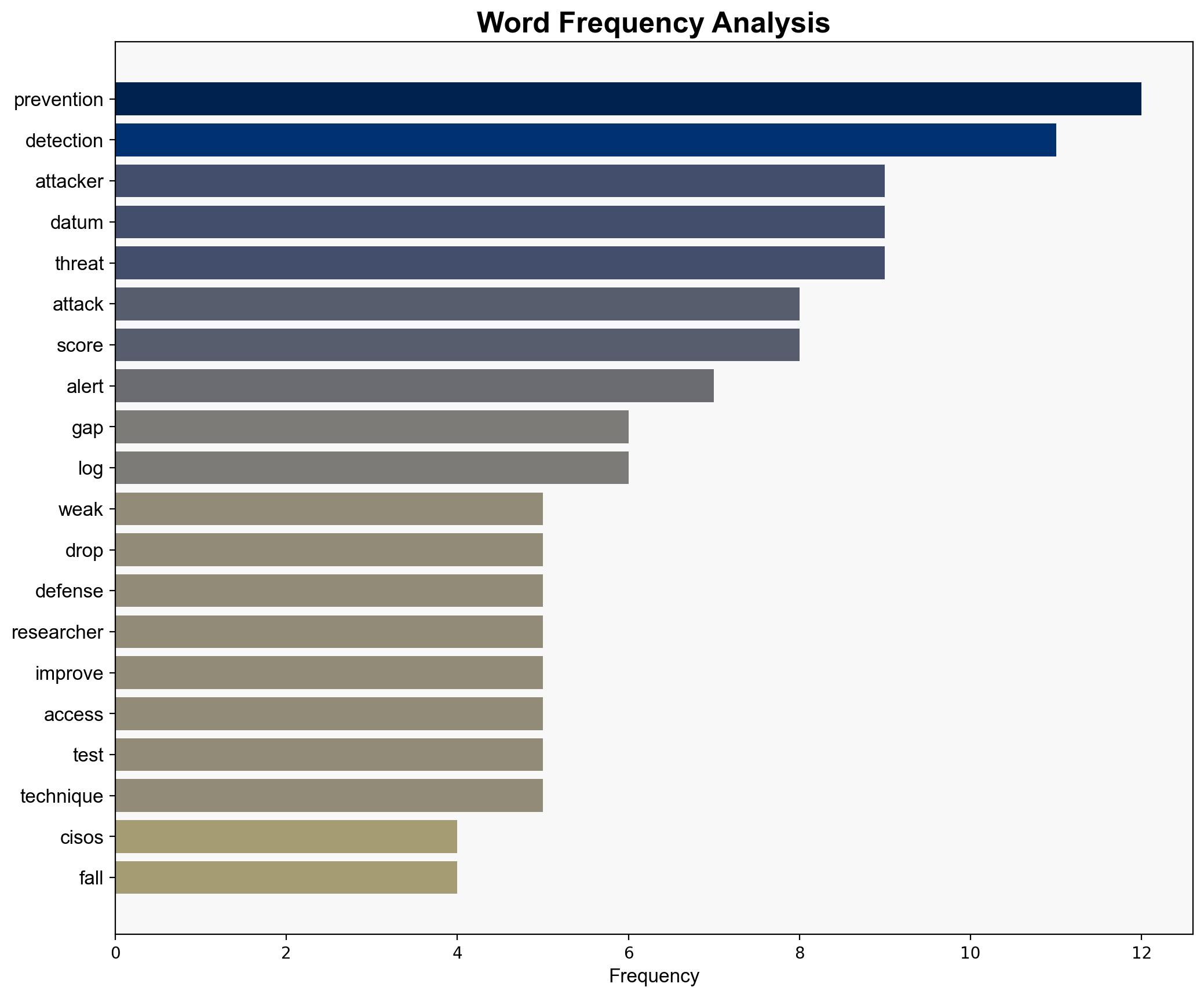
The most supported hypothesis is that the current cybersecurity measures are insufficient to counter evolving threats, leading to increased risk levels for CISOs. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to the reliance on simulated attack data and potential reporting biases. Recommended action includes enhancing detection capabilities and regularly updating security protocols to adapt to new threat vectors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The increase in risk levels is primarily due to inadequate alerting and prevention mechanisms that fail to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The perceived increase in risk is exaggerated due to over-reliance on simulated attack data and may not accurately reflect real-world threat levels.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported. The data indicates a significant drop in prevention effectiveness and a rise in successful attack simulations, suggesting real vulnerabilities. Hypothesis B is less supported as it does not adequately account for the consistent trends observed across multiple simulations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that simulated attacks accurately represent real-world scenarios. Another assumption is that the data provided by Picus Security is comprehensive and unbiased.
– **Red Flags**: The reliance on simulations could introduce bias if these do not accurately mimic current threat landscapes. There is also a potential blind spot in the regional focus of the data, which may not account for global threat variations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The current gaps in cybersecurity could lead to increased data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage for organizations. These vulnerabilities may also be exploited by state-sponsored actors, escalating geopolitical tensions. The economic impact could be significant if critical infrastructure is targeted, leading to broader national security concerns.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance detection capabilities by integrating advanced threat intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
- Regularly update and test security protocols against the latest threat vectors through real-world simulations.
- Scenario-based projections:
- **Best Case**: Improved detection and prevention mechanisms lead to a significant reduction in successful cyberattacks.
- **Worst Case**: Continued gaps in cybersecurity result in a major breach affecting critical infrastructure.
- **Most Likely**: Incremental improvements in security measures reduce some risks, but new threats continue to emerge.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Dr. Suleyman Ozarslan, associated with Picus Labs, is a key figure in the analysis and recommendations provided in the report.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus