West Coast Marines aim to train 500 drone pilots annually through intensive 15-day crash course.
Published on: 2026-02-09
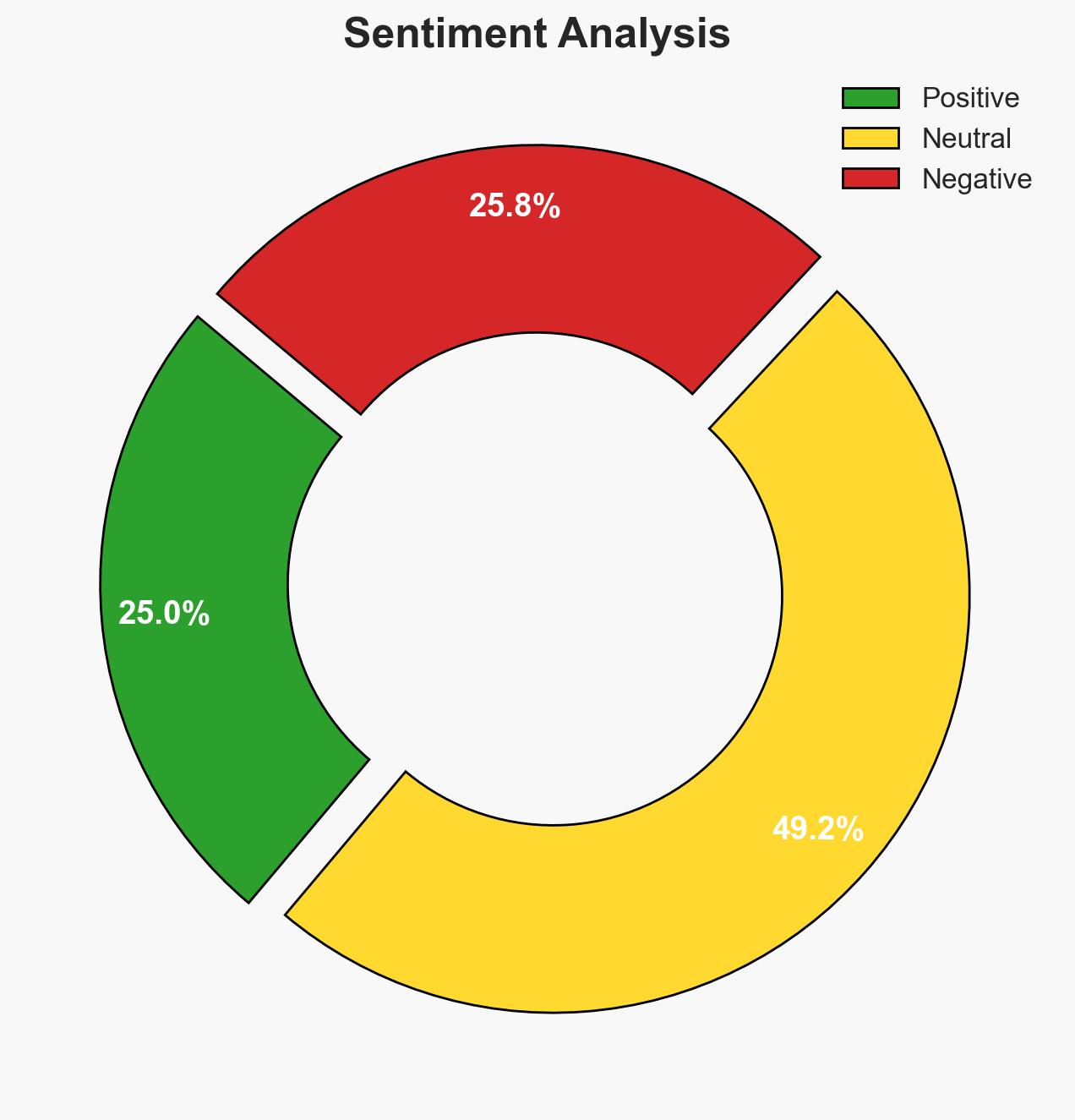
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: West Coast Marines want to train 500 new drone pilots a year in a crash course on everything from flying to explosions
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The U.S. Marine Corps is accelerating its drone pilot training program, aiming to certify 500 operators annually through an intensive 15-day course. This initiative reflects a strategic shift towards rapid adoption of drone technology, influenced by recent battlefield experiences in Ukraine. The program’s success could significantly enhance the Marines’ operational capabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the limited data on long-term outcomes and potential challenges in scaling the program.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Marine Corps’ accelerated training program will successfully integrate drone operations across the force, enhancing tactical capabilities. This is supported by the structured training approach and lessons learned from Ukraine. However, uncertainties include the scalability of the program and the adaptability of Marines to new technologies.
- Hypothesis B: The rapid training initiative may face significant challenges, such as resource constraints and potential skill gaps, limiting its effectiveness. Contradicting evidence includes the relatively short duration of the course and the complexity of drone operations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured nature of the training and the strategic emphasis on rapid modernization. Indicators such as successful graduation rates and operational deployment outcomes could further validate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The training program will receive sustained funding and institutional support; Marines will adapt quickly to drone technology; battlefield lessons from Ukraine are applicable to U.S. operations.
- Information Gaps: Long-term effectiveness of the training program; detailed performance metrics of trained operators in operational settings; potential logistical or technical challenges in scaling the program.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias in evaluating the program’s success based on initial enthusiasm; potential underreporting of challenges or failures; over-reliance on lessons from a different geopolitical context (Ukraine).
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could significantly alter the tactical landscape for the U.S. Marine Corps, with broader implications for military strategy and international security dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Enhanced drone capabilities may shift power dynamics in regions where the U.S. is engaged, potentially escalating tensions with adversaries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved drone operations could enhance counter-terrorism efforts, but also increase the risk of collateral damage and civilian casualties.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased reliance on drones may expose vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks and necessitate robust cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: The program could drive demand for drone-related technologies and skills, impacting the defense industry and labor market.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor training outcomes and gather feedback from participants; assess resource allocation and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with industry for technological advancements; implement resilience measures against cyber threats; evaluate long-term program sustainability.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful integration and enhanced operational capabilities; Worst: Program fails to scale, leading to resource wastage; Most-Likely: Gradual improvement with iterative adjustments based on feedback and operational needs.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- 1st Lt. Braeden McClain, Infantry Officer overseeing the course
- Neros, drone manufacturer
- U.S. Marine Corps
- Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, drone warfare, military training, defense modernization, tactical innovation, cybersecurity, geopolitical strategy, defense industry
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us