What 50 companies got wrong about cloud identity security – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-07-25
Intelligence Report: What 50 companies got wrong about cloud identity security – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
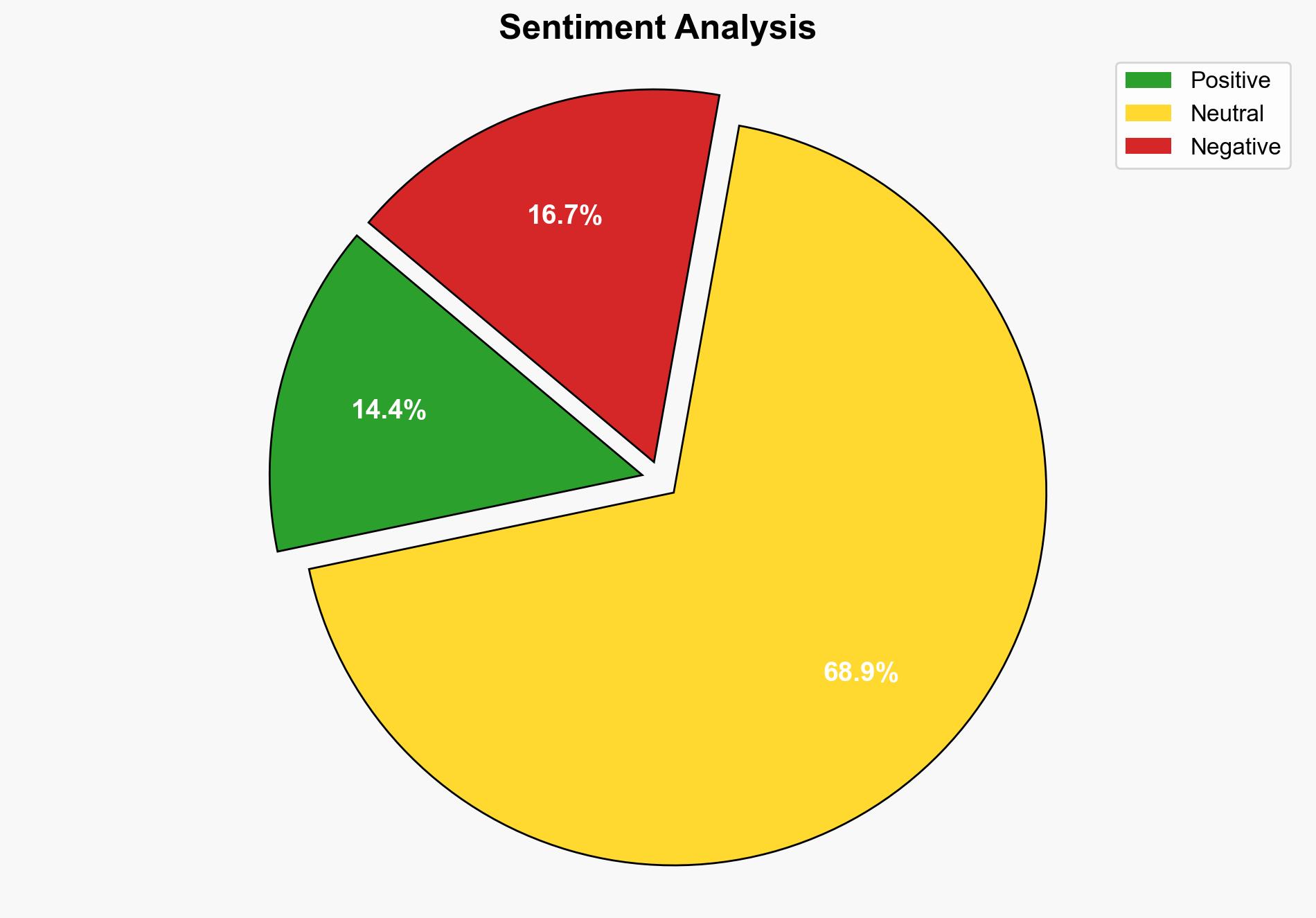
The most supported hypothesis is that companies are failing to implement basic cloud identity security controls, leading to significant vulnerabilities. This conclusion is drawn with a moderate confidence level due to the consistent identification of common security gaps across multiple organizations. Recommended actions include prioritizing the implementation of foundational security measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular audits to mitigate risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Companies are neglecting basic cloud identity security controls due to a lack of awareness or understanding of the risks involved. This results in widespread vulnerabilities and compliance violations.
Hypothesis 2: Companies are aware of the necessary security measures but are unable to implement them effectively due to resource constraints, leading to persistent security gaps.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported by the data, as the report highlights common issues such as missing MFA and poor separation of duties, suggesting a fundamental lack of awareness or prioritization of these controls.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that companies have the necessary resources and knowledge to implement basic security controls. A potential cognitive bias is the assumption that all companies face the same level of threat and resource availability. A red flag is the lack of detailed data on why specific controls are not implemented, which could indicate either a reporting bias or a gap in understanding the root causes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The failure to address basic security controls could lead to increased incidents of data breaches and ransomware attacks, escalating costs for cyber insurance, and potential regulatory fines. Economically, this could impact company valuations and investor confidence. Geopolitically, widespread vulnerabilities could be exploited by state actors, increasing national security risks. Psychologically, repeated breaches could erode public trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement MFA for all administrative accounts immediately to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Conduct regular security audits and compliance checks to identify and address gaps.
- Invest in employee training to raise awareness of security best practices.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Companies rapidly adopt recommended security measures, leading to a significant reduction in breaches.
- Worst Case: Continued neglect results in a major data breach affecting multiple organizations, leading to regulatory crackdowns.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements are made, but some vulnerabilities persist due to resource constraints.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Santhosh Jayaprakash (CEO of Unosecur) is a key individual mentioned in the report, providing insights into the security landscape.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, compliance, cloud security, risk management