Whats Your Cybersecurity Maturity – Trendmicro.com
Published on: 2025-09-10
Intelligence Report: Whats Your Cybersecurity Maturity – Trendmicro.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
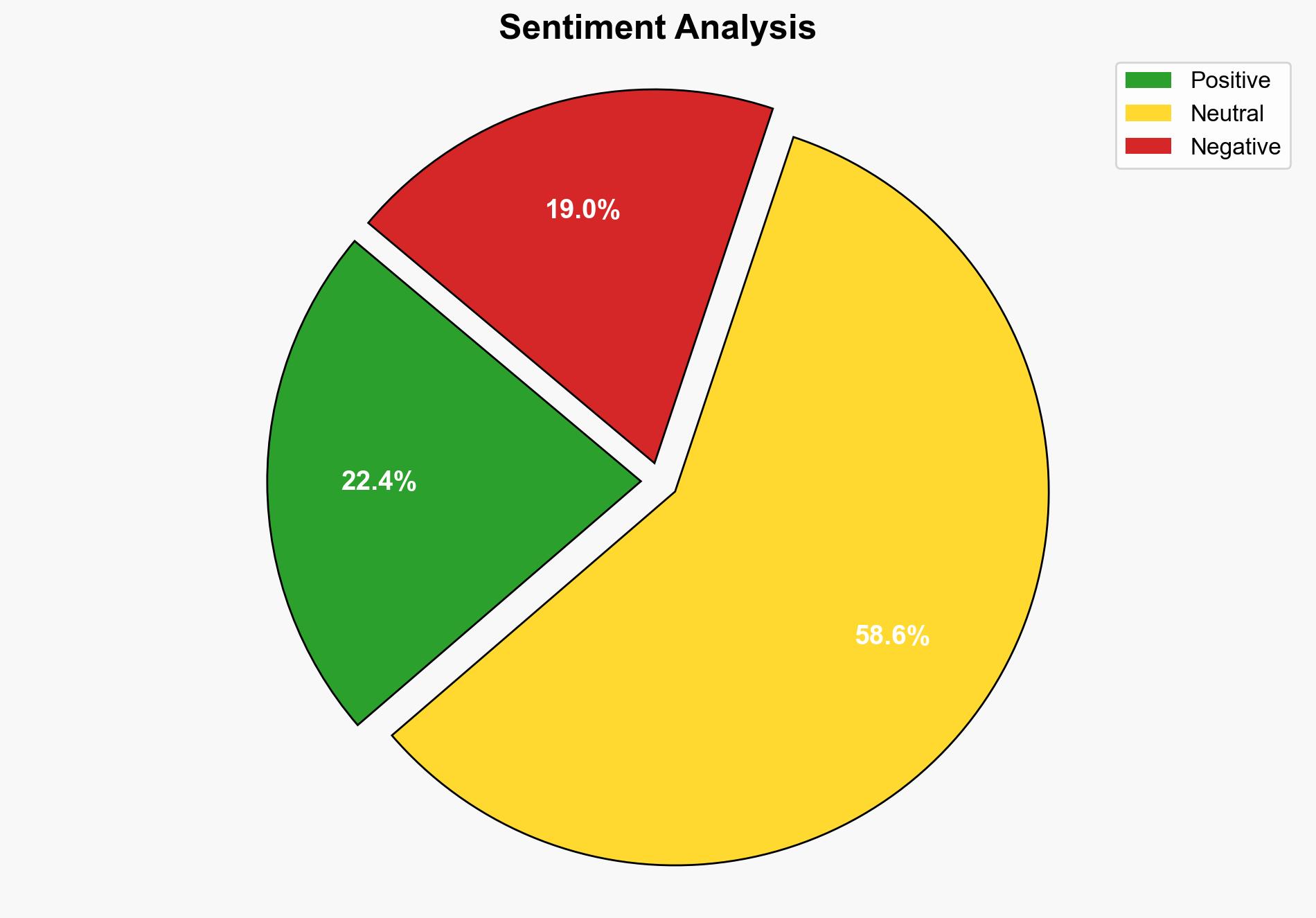
The analysis suggests that organizations are at varying stages of cybersecurity maturity, with a significant number still in reactive or tactical modes. The most supported hypothesis is that many organizations lack comprehensive visibility and automated processes, which limits their ability to proactively manage cyber risks. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Organizations should prioritize transitioning to a risk-driven, proactive cybersecurity approach by enhancing automation and integrating advanced technologies like AI and machine learning.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Most organizations are still in the early stages of cybersecurity maturity, primarily operating in reactive or tactical modes, which limits their ability to effectively manage and mitigate cyber threats.
2. **Hypothesis B**: Organizations are progressively advancing towards a proactive cybersecurity maturity stage, leveraging automation and strategic alignment with business objectives to manage risks more effectively.
Using Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH), Hypothesis A is better supported by the evidence provided. The source indicates that many organizations struggle with visibility and rely on outdated methods, suggesting a predominance of reactive and tactical stages.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the progression through cybersecurity maturity stages is linear and that all organizations have equal access to resources for advancement.
– **Red Flags**: The lack of specific data on the proportion of organizations at each maturity stage could lead to overgeneralization. There is also an assumption that technological solutions alone can address all cybersecurity challenges.
– **Blind Spots**: The potential impact of organizational culture and leadership on cybersecurity maturity is not addressed.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Implications**: Organizations in reactive or tactical modes are more vulnerable to cyber threats, which could lead to increased incidents of data breaches and financial losses.
– **Strategic Risks**: Failure to advance in cybersecurity maturity could result in reputational damage and regulatory penalties. There is also a risk of cascading effects on supply chains and critical infrastructure.
– **Economic and Geopolitical Dimensions**: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the economic impact of cyber incidents could escalate, affecting national security and international relations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Organizations should conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify gaps in their cybersecurity posture.
- Invest in automation and advanced technologies to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Rapid adoption of proactive measures leads to a significant reduction in cyber incidents.
- Worst Case: Continued reliance on reactive measures results in severe data breaches and financial losses.
- Most Likely: Gradual improvement in cybersecurity maturity with incremental adoption of proactive strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned in the source text. The focus is on organizations and their cybersecurity maturity levels.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus