Widespread Exploitation of Patched WinRAR Vulnerability by Various Threat Actors
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Everybody is WinRAR phishing dropping RATs as fast as lightning
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
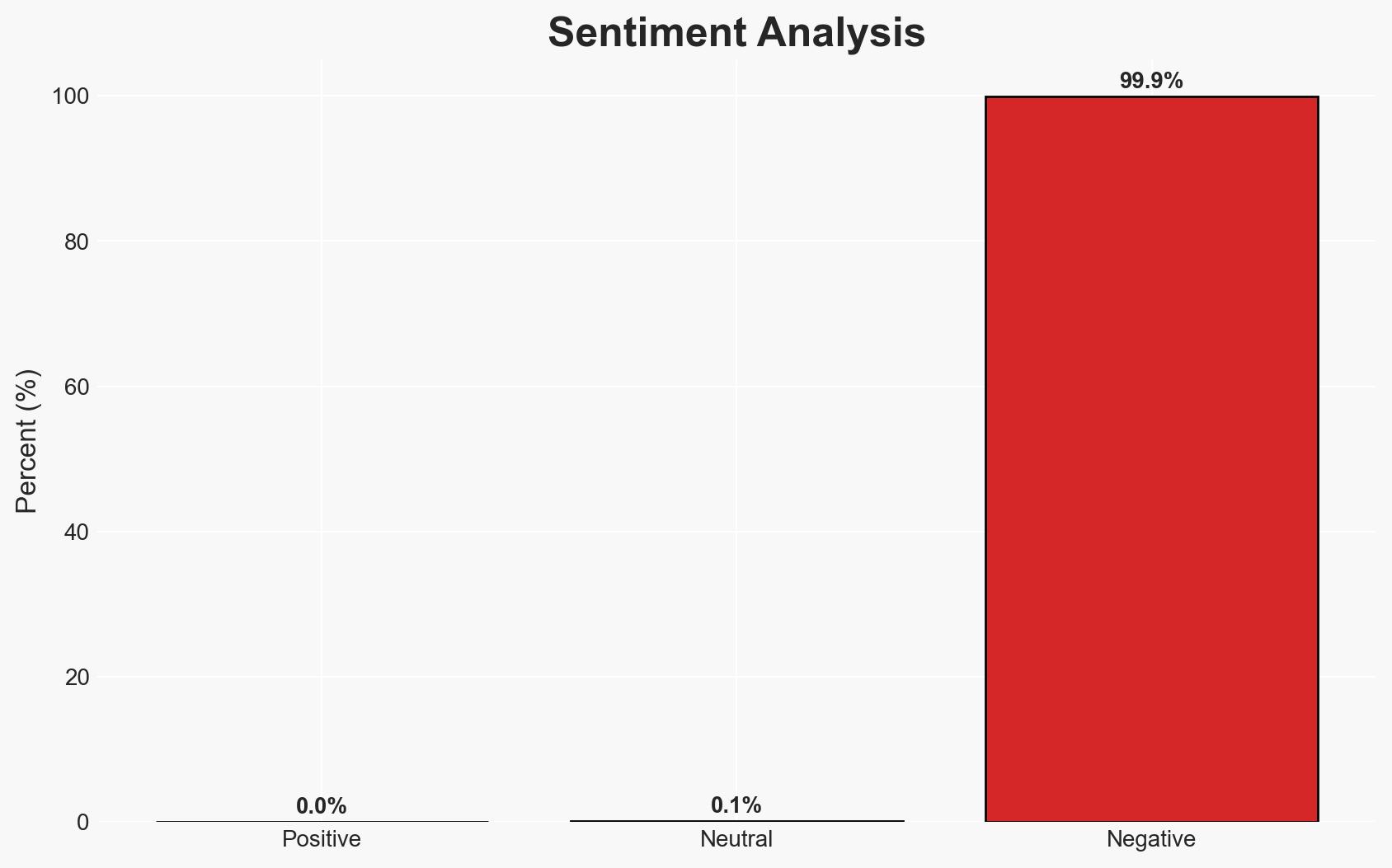
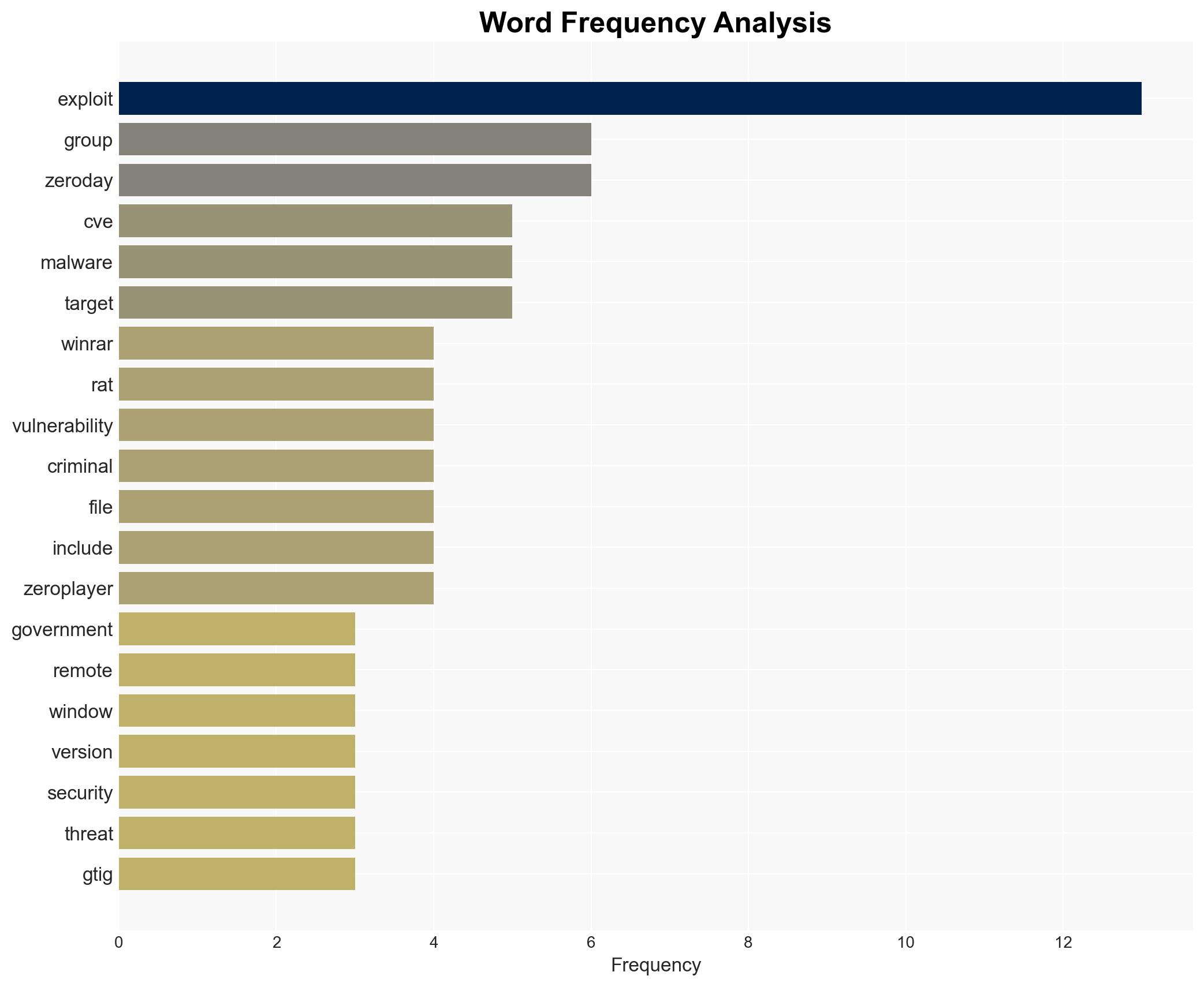
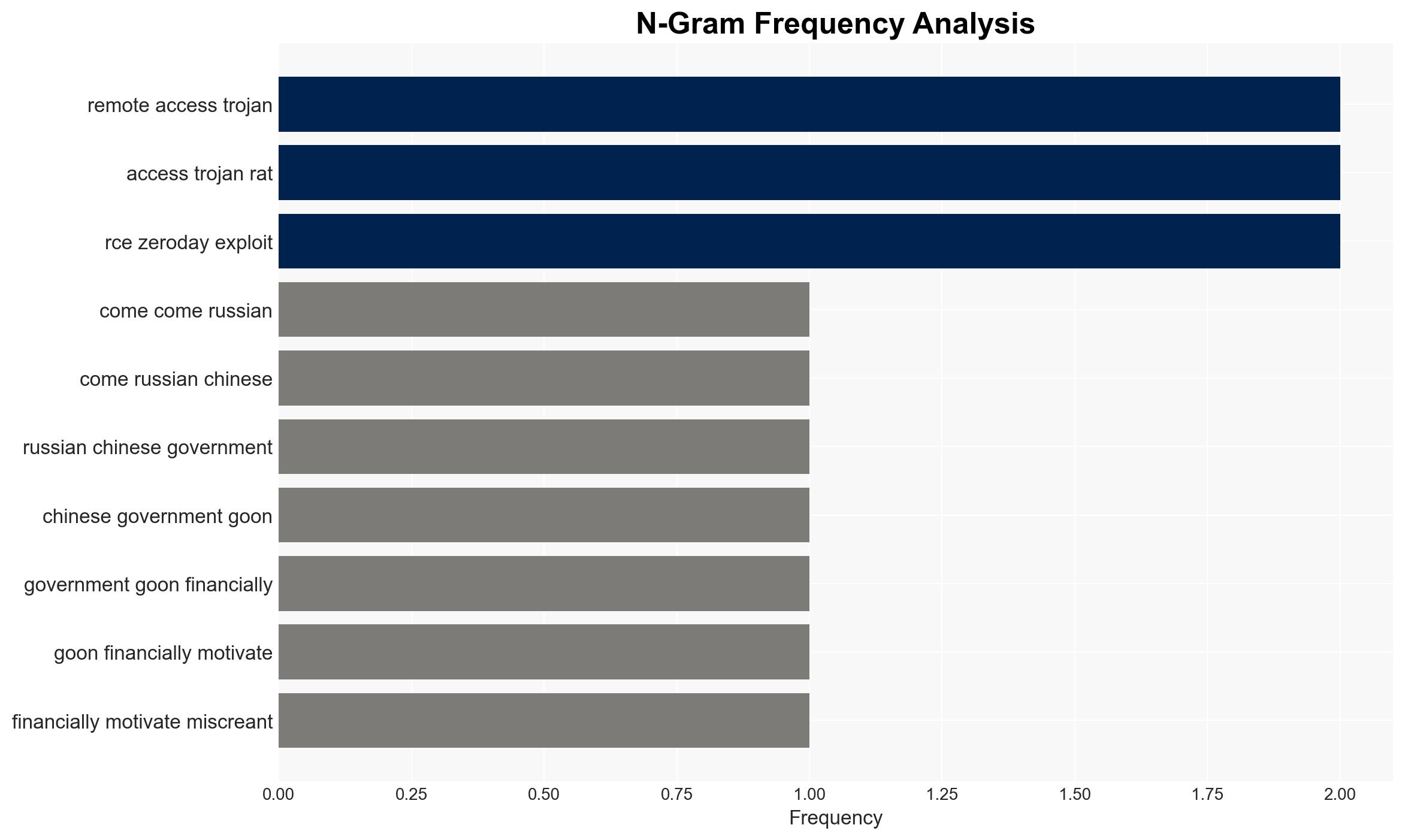
Exploitation of the WinRAR vulnerability CVE-2025-8088 by state-backed and criminal actors poses a significant threat to military, government, and commercial sectors globally. The vulnerability, although patched, continues to be exploited, indicating persistent security gaps. The most likely hypothesis is that these actors will continue leveraging this exploit due to its effectiveness and the slow patch adoption rate. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: State-backed and criminal actors will continue exploiting CVE-2025-8088 due to its proven effectiveness and the slow adoption of patches. Supporting evidence includes ongoing exploitation reports and the involvement of multiple sophisticated threat actors. Key uncertainties include the rate of patch adoption and potential countermeasures by affected organizations.
- Hypothesis B: Exploitation of CVE-2025-8088 will decline as organizations patch their systems and develop countermeasures. This is contradicted by the persistent exploitation despite the availability of a patch, suggesting that patch adoption is not widespread.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the continuous reports of exploitation and the involvement of multiple actors. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant increase in patch adoption or effective countermeasures being widely implemented.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations are slow to adopt patches; threat actors have the capability to exploit the vulnerability effectively; geopolitical tensions drive state-backed exploitation.
- Information Gaps: Exact patch adoption rates across affected sectors; detailed motivations and objectives of the involved threat actors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from security firms with vested interests; possible deception by threat actors to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued exploitation of CVE-2025-8088 could exacerbate geopolitical tensions, particularly involving state-backed actors targeting Ukraine. The persistence of this threat highlights vulnerabilities in cybersecurity practices and patch management.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation of cyber operations in geopolitical hotspots, particularly involving Russia and China.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to national security infrastructure and critical sectors, necessitating enhanced cybersecurity measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread data breaches and espionage activities, impacting information integrity and confidentiality.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts due to disruptions in commercial sectors and loss of consumer trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage rapid patch adoption across vulnerable systems; increase monitoring for signs of exploitation; enhance user awareness and training on phishing tactics.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on emerging threats; invest in advanced threat detection and response capabilities; promote resilience through regular security audits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption and effective countermeasures lead to a decline in exploitation.
- Worst: Continued exploitation results in significant breaches and geopolitical tensions.
- Most-Likely: Ongoing exploitation with gradual improvement in defenses as awareness and patching increase.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- RomCom
- APT44 (Frozenbarents)
- Temp.Armageddon (Carpathian)
- Turla (Summit)
- Unnamed PRC-based group
- zeroplayer
- Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG)
- ESET researchers
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, state-sponsored attacks, vulnerability exploitation, patch management, cyber-espionage, geopolitical tensions, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us