World Health Organization CISO on securing global health emergencies – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-07-21
Intelligence Report: World Health Organization CISO on Securing Global Health Emergencies – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
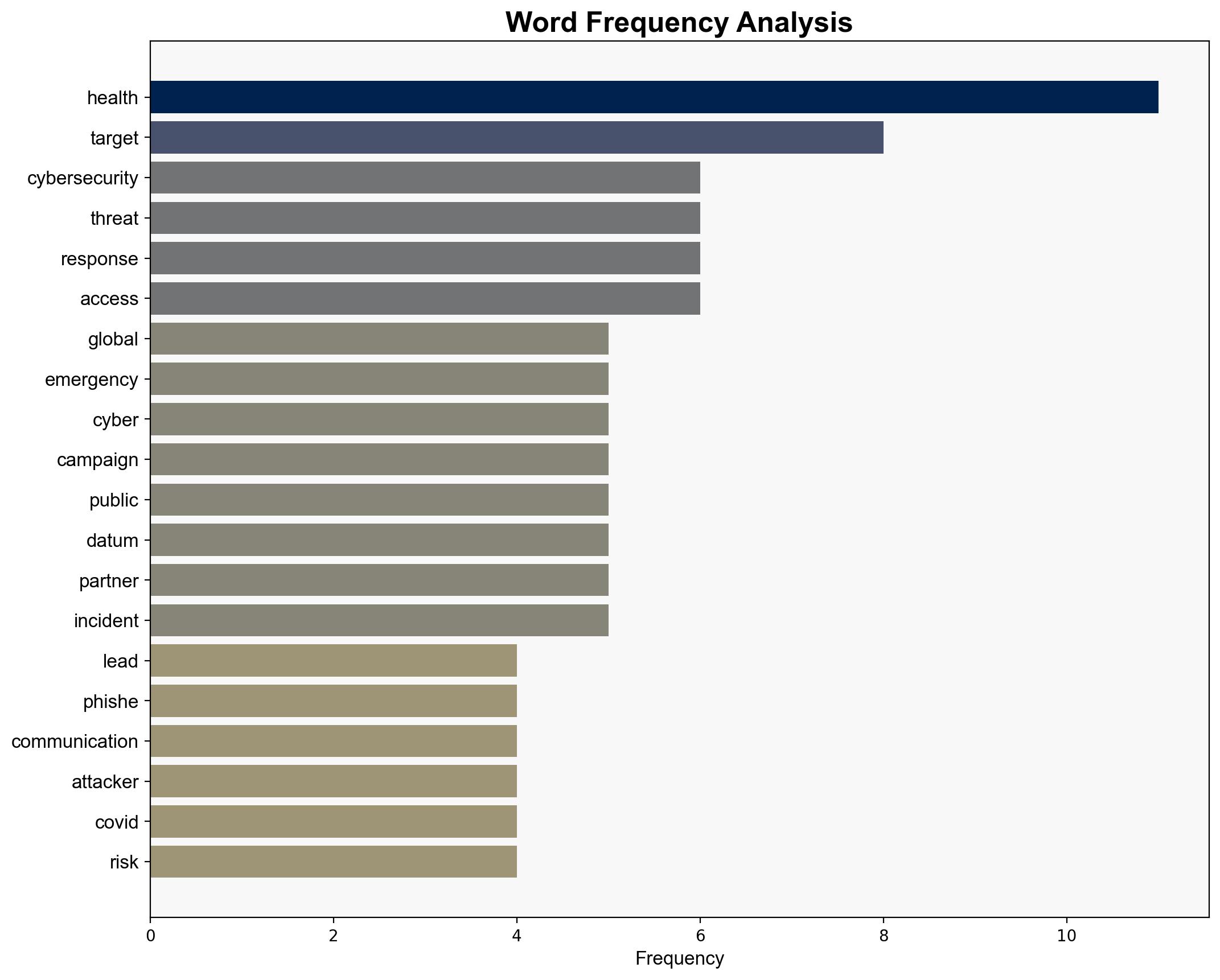
The World Health Organization (WHO) is enhancing its cybersecurity measures to address the increased risk of cyber threats during global health emergencies. Key strategies include removing fake websites, issuing public warnings, and securing data sharing with global partners. The organization is focused on developing a comprehensive cyber response strategy that includes realistic simulation exercises to identify and rectify critical gaps in decision-making and incident containment.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied to ensure methodological consistency:
Adversarial Threat Simulation
Simulations reveal that cyber threats, such as phishing and ransomware attacks, tend to spike during global health emergencies, exploiting vulnerabilities and misinformation.
Indicators Development
Monitoring systems for anomalies is crucial for early detection of threats, particularly those targeting vaccine research and public trust.
Bayesian Scenario Modeling
Forecasting suggests a high likelihood of increased cyber exploitation during health crises, necessitating robust preventive measures.
Network Influence Mapping
Mapping influence relationships helps assess the impact of threat actors and improve strategic responses.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated a fivefold increase in phishing attempts, with attackers impersonating leadership and targeting hospitals. The strategic risks include potential disruptions to healthcare services and compromised vaccine research. The systemic vulnerabilities are exacerbated by misinformation campaigns that undermine public trust.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance collaboration with digital risk partners to dismantle fraudulent sites swiftly.
- Implement strict encryption and access control measures to secure data sharing, especially in low-resource settings.
- Conduct regular cybersecurity training for staff to improve incident response readiness.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Strengthened global cybersecurity collaboration mitigates threats effectively.
- Worst Case: Persistent cyber attacks lead to significant disruptions in healthcare delivery.
- Most Likely: Continued adaptation and improvement of cybersecurity protocols reduce impact over time.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
Flavio Aggio
6. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, global health, misinformation, data protection