Yemen’s Control Landscape in 2026: PLC Regains Provinces Amid Rising Tensions with STC and Regional Powers
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Mapping who controls what in Yemen in 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
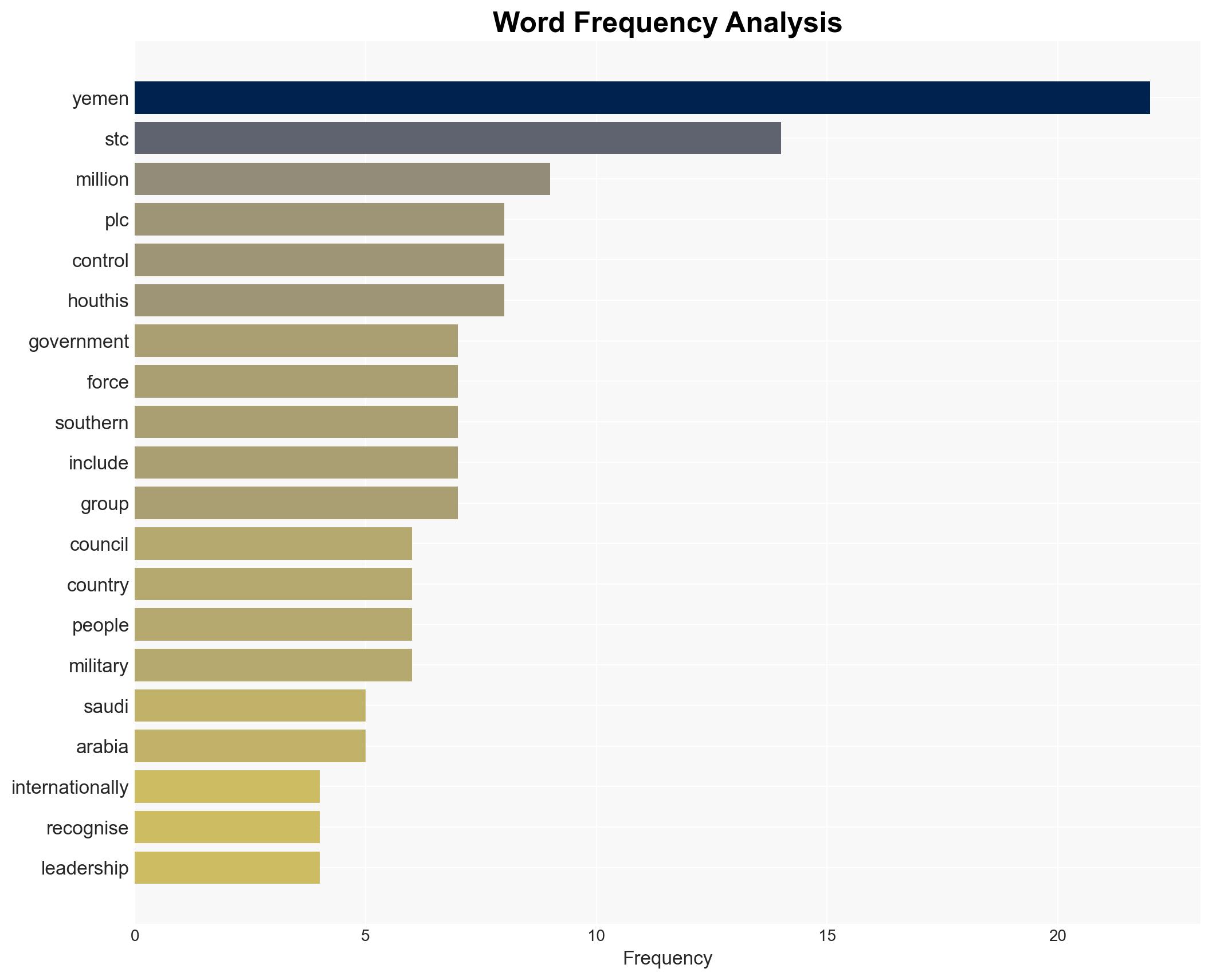
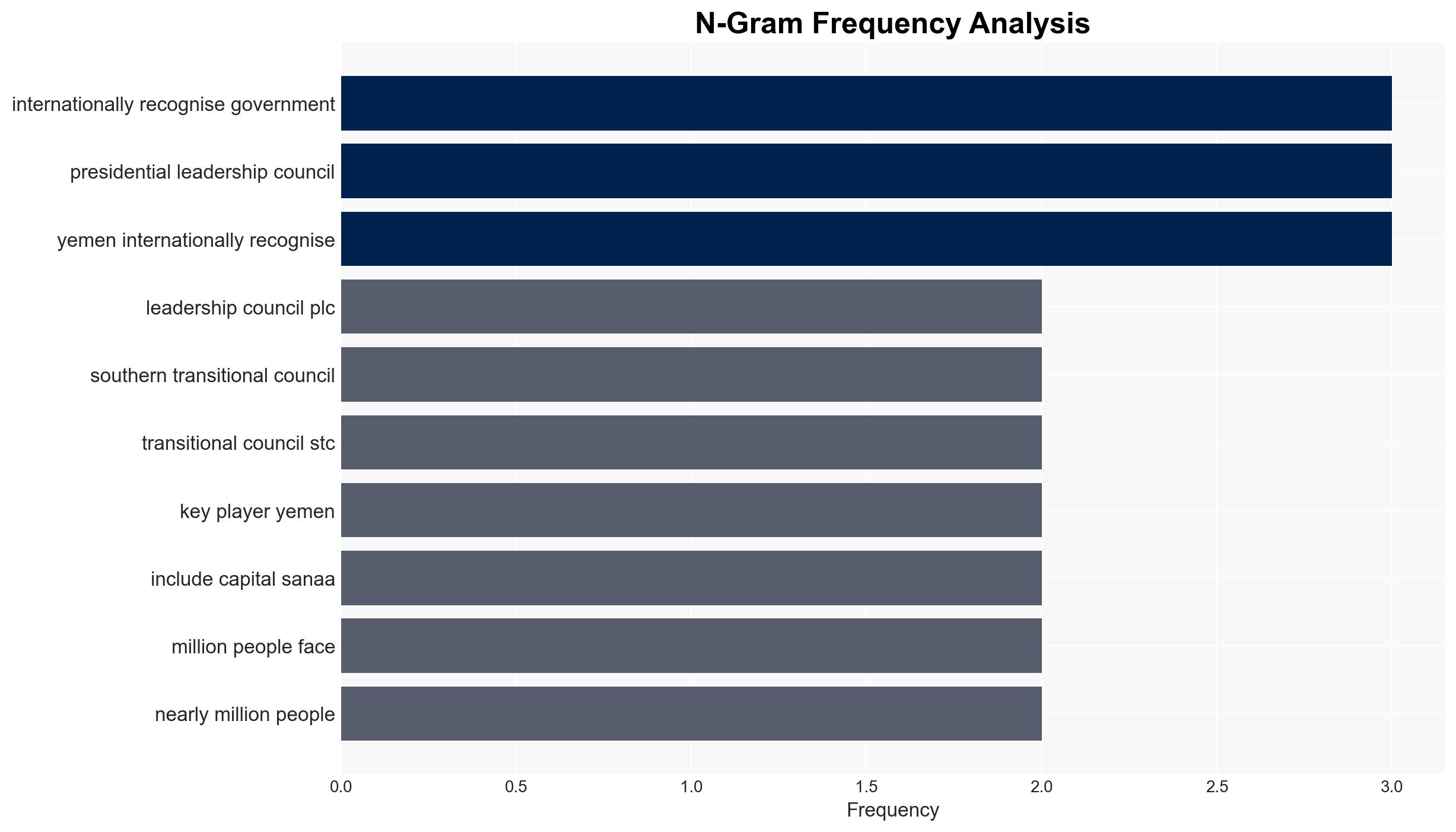
The recent recapture of strategic provinces by the Presidential Leadership Council (PLC) from the Southern Transitional Council (STC) marks a significant shift in Yemen’s power dynamics, potentially exacerbating tensions between Saudi Arabia and the UAE. The PLC’s actions, supported by Saudi airstrikes, underscore the fragile alliances and complex geopolitical interests in the region. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, considering the fluidity of alliances and limited visibility into internal decision-making processes.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The PLC’s recapture of Hadramout and al-Mahra will stabilize its control and deter further STC aggression. Supporting evidence includes Saudi military backing and the strategic importance of these provinces. However, uncertainties remain about the STC’s capacity to regroup and the UAE’s future support.
- Hypothesis B: The STC will continue its secessionist efforts, potentially escalating conflict with the PLC. This is supported by the STC’s historical pursuit of southern independence and recent actions. Contradicting evidence includes the loss of key territories and leadership challenges.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the PLC’s regained territorial control and Saudi backing. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include renewed UAE support for the STC or significant internal dissent within the PLC.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The PLC maintains Saudi support; the STC lacks immediate capacity for a counter-offensive; UAE support for the STC remains limited; internal PLC cohesion is stable.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on UAE’s strategic intentions, STC’s internal dynamics, and PLC’s long-term governance strategy.
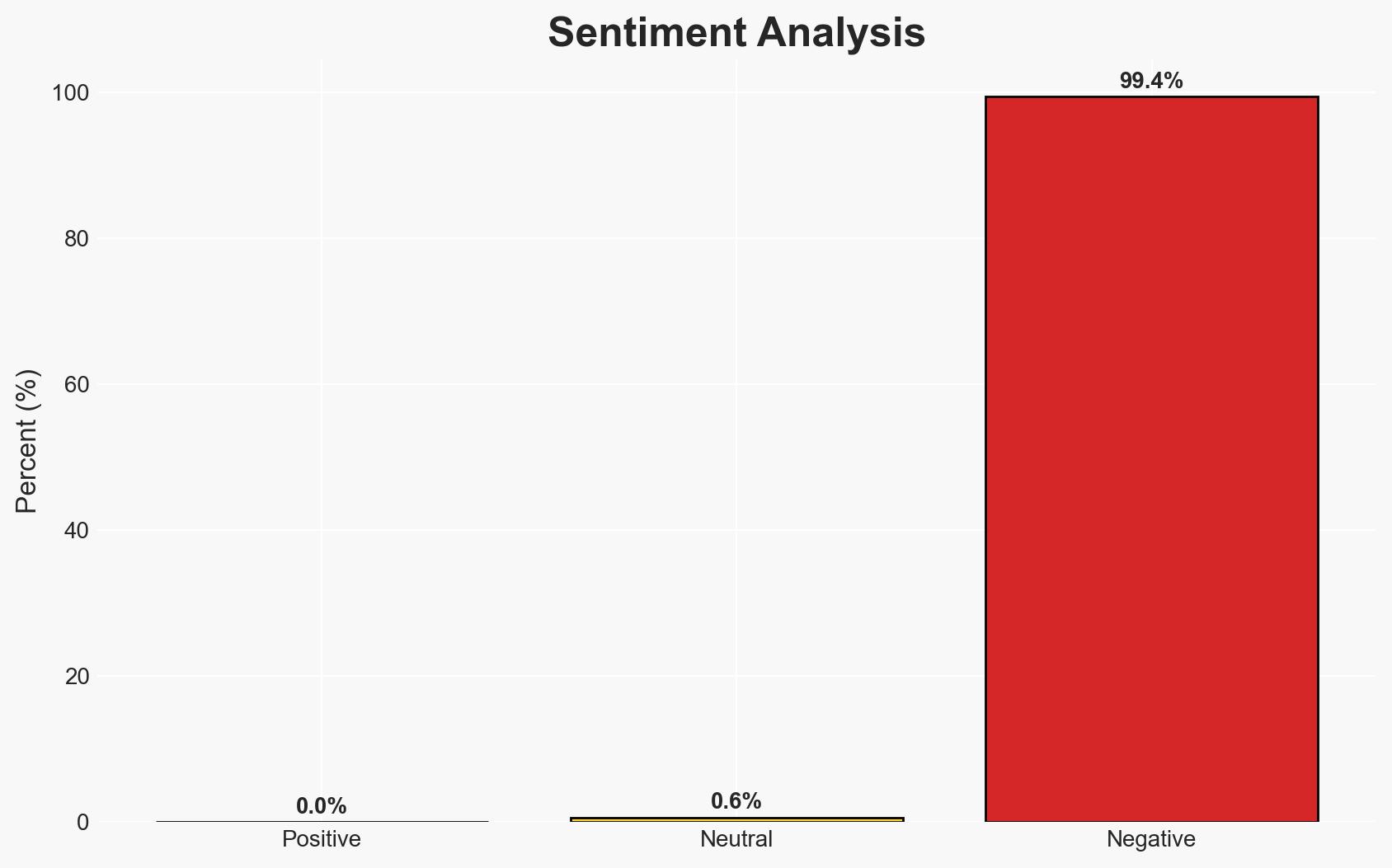
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential source bias from Saudi and UAE media; risk of deception in reported military capabilities and intentions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolving power struggle in Yemen could lead to increased regional instability, affecting geopolitical alignments and humanitarian conditions. The situation remains volatile, with potential for rapid shifts in alliances and territorial control.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation of Saudi-UAE tensions; potential realignment of regional alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of opportunistic actions by Houthi forces exploiting internal divisions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting regional actors; information warfare to sway public opinion.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of oil production and trade routes; exacerbation of humanitarian crisis affecting millions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on STC and UAE activities; engage in diplomatic efforts to mediate between Saudi Arabia and UAE.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances; support humanitarian aid initiatives to mitigate civilian impact.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mediation leads to a ceasefire and political negotiations.
- Worst: Escalation into a broader regional conflict involving direct UAE-Saudi confrontation.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-intensity conflict with periodic escalations and shifting territorial control.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Rashad al-Alimi – Leader of the Presidential Leadership Council
- Aidarous al-Zubaidi – Former leader of the Southern Transitional Council
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other key individuals.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, Yemen conflict, regional alliances, Saudi-UAE relations, secessionist movements, geopolitical instability, humanitarian crisis, oil-rich provinces
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us